Video Lecture
Theory For Notes Making
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Objective Assignment
Q.1
An object is placed at a distance of 3f from a convex lens of focal length f. A slab of refractive index m is placed in between lens and object. The image of the object will be formed nearest to the object if thickness of the slab is
(a) f
(b) 2f
(c) \frac{f}{{\mu -1}}
(d) \frac{{\mu f}}{{\mu -1}}
Ans. (d)
Q.2
A concave lens of focal length 10 cm and a convex lens of focal length 20 cm are placed certain distance apart. If parallel rays incident on one lens become converging after passing through other lens, then the separation between the lenses must be greater than
(a) zero (b) 5 cm (c) 10 cm (d) 9 cm
Ans. (c)
Q.3
The distance between an object and the screen is 100 cm. A lens produces an image on the screen when placed at either of the positions 40 cm apart. The power of the lens is nearly
(a) 3 dioptres (b) 5 dioptres (c) 7 dioptres (d) 9 dioptres
Ans. (b)
Q.4
If two lenses of power +5 diopters are mounted at some distance apart, the combination will always behave like a diverging lens if the distance between them is
(a) Greater than 40 cm
(b) Equal than 40 cm
(c) Equal to 10 cm
(d) Less than 10 cm
Ans. (a)
Q.5
A convex lens of focal length 12 cm is made of glass of m = \frac{3}{2}. What will be its focal length when immersed in liquid of m = \frac{5}{4}
(a) 6 cm (b) 12 cm (c) 24 cm (d) 30 cm
Ans. (d)
Q.6
A lens of power +2 diopters is placed in contact with a lens of power –1 diopter. The combination will behave like
(a) A convergent lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A divergent lens of focal length 100 cm
(c) A convergent lens of focal length 100 cm
(d) A convergent lens of focal length 200 cm
Ans. (c)
Q.7
A concave lens of focal length F produces an image equal to 1/n of size of object, the distance of the image, from the lens is
(a) (n+1)F
(b) (n-1)F
(c) \left( {\frac{{n+1}}{n}} \right)F
(d) \left( {\frac{{n-1}}{n}} \right)F
Ans. (d)
Q.8
A convex lens A of focal length 20 cm and a concave lens B of focal length 5 cm are kept along the same axis with a distance d between them. If a parallel beam of light falling on A leaves B as a parallel beam, then the distance d in cm will be
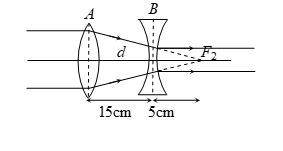
(a) 25 (b) 15 (c) 30 (d) 50
Ans. (b)
Q.9
Two convex lenses placed in contact form the image of a distant object at P. If the lens B is moved to the right, the image will
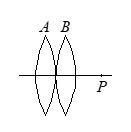
(a) move to the left
(b) move to the right
(c) remain at P
(d) move either to the left or right, depending upon focal lengths of the lenses
Ans. (b)
Subjective Assignment
Q.1
Under what condition does a biconvex lens of glass having a certain refractive index act as a plane glass sheet when immersed in a liquid ?
Q.2
How would a biconvex lens appear when placed in a trough of liquid having the same refractive index as that of the lens ?
Q.3
A convex lens is placed in contact with a plane mirror. A point object at a distance of 20 cm on the axis of this combination has its image coinciding with itself. What is the focal length of the lens ?
Q.4
Two thin lenses of power +6D and –2D are in contact. What is the focal length of the combination ?
Q.5
Why are convex mirrors used as side view mirrors in cars ?
Q.6
A converging lens is kept coaxially in contact with a diverging lens-both the lenses being of equal focal lengths. What is the focal length of the combination ?
Q.7
An object of size 3.0cm is placed 14cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 21cm. Describe the image produced by the lens. What happens if the object is moved further away from the lens?
Q.8
What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses.
Q.9
A beam of light converges at a point P. A concave lens of focal length 16 cm is placed in the path of this beam 12 cm from P. Draw a ray diagram and find the location of the point at which the beam would now converge.
Q.10
A screen is placed 90cm from an object. The image of the object on the screen is formed by a convex lens at two different locations separated by 20cm. Determine the focal length of the lens.
Q.11
An illuminated object and a screen are placed 90 cm apart. Determine the focal length and nature of the lens required to produce a clear image on the screen, twice the size of the object..
Q.12
The image obtained with a convex lens is erect and its length is four times the length of the object. If the focal length of the lens is 20 cm, calculate the object and image distances.
Q.13
A convex lens is used to obtain a magnified image of an object on a screen 10 m the lens. If the magnification is 19, find the focal length of the lens.
Q.14
The image of a small electric bulb fixed on the wall of a room is to be obtained on the opposite wall 3m away by means of a large convex lens. What is the maximum possible focal length of the lens required for the purpose?
Q.15
(a) Determine the ‘effective focal length’ of the combination of the two lenses, a convex lens of focal length 30cm and a concave lens of focal length 20cm, if they are placed 8.0cm apart with their principal axes coincident. Does the answer depend on which side of the combination a beam of parallel light is incident? Is the notion of effective focal length of this system useful at all?
(b) An object 1.5 cm in size is placed on the side of the convex lens in the arrangement (a) above. The distance between the object and the convex lens is 40cm. Determine the magnification produced by the two-lens system, and the size of the image.
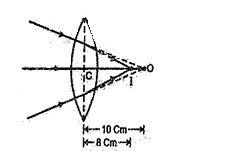
16.
Rays of light fall in on a convex lens of focal length 40 cm. as shown in fig. Determine the position of the image.