Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
Q.1
The principle of optical fibre is
(a) Diffraction
(b) Polarisation
(c) Interference
(d) Total Internal reflection
Ans. (d)
Q.2
A ray of light strikes a glass plate at an angle of 60° with the vertical. If the reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other, the refractive index of glass is
(a) \frac{{\sqrt{3}}}{2}
(b) \frac{3}{2}
(c) \frac{1}{2}
(d) \sqrt{3}
Ans. (d)
Q.3
Light travels through a glass plate of thickness t and having refractive index m. If c be the velocity of light in vacuum, the time taken by the light to travel this thickness of glass is
(a) \frac{t}{{\mu \ c}}
(b) t m c
(c) \frac{{\mu \,t}}{c}
(d) \frac{{\mu \,t}}{c}
Ans. (c)
Q.4
The length of a vertical pole above the surface of a lake of water (n = 4/3) is 24 cm. To an under-water fish just below the water surface the tip of the pole appears to be
(a) 18 cm above the surface
(b) 24 cm above the surface
(c) 32 cm above the surface
(d) 36 cm above the surface
Ans. (c)
Q.5
A ray incident at a point at an angle of incidence of 600 enters a glass sphere of R.1. and gets reflected and refracted at the farther surface of the sphere. The angle between the reflected and refracted rays at this surface is
(a) 500 (b) 600 (c) 900 (d) 400
Ans. (c)
Q.6
A circular beam of light of diameter d = 2 cm falls on a plane surface of glass. The angle of incidence is 600 and refractive index of glass is m = 3/2. The diameter of the refracted beam is
(a) 4.0 cm (b) 3.0 cm (c) 3.26 cm (d) 2.52 cm
Ans. (c)
Q.7
Light wave enters from medium 1 to medium 2. Its velocity in 2nd medium is double from 1st. For total internal reflection the angle of incidence must be greater than
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 45° (d) 90°
Ans. (a)
Q.8
The refractive index of water is 4/3 and that of glass is 5/3. Then the critical angle for a ray of light entering in water from glass will be
(a) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}\left( {\frac{4}{5}} \right)
(b) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}\left( {\frac{5}{4}} \right)
(c) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}\left( {\frac{{20}}{9}} \right)
(d) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}\left( {\frac{9}{{20}}} \right)
Ans. (a)
Q.9
A plano-convex lens has a thickness of 4 cm. When placed on a horizontal table with curved surface in contact with it, the apparent depth of the bottom most point of the lens is found to be 3 cm. If the lens is inverted such that the plane face is in contact with the table, the apparent depth of the centre of plane face is found to be 25/8 cm. The focal length of the lens is
(a) 50 cm (b) 75 cm (c) 100 cm (d) 150 cm
Ans. (b)
Q.10
A light ray falls on a square slab at an angle 45°. What must be the minimum index of refraction of glass, if total internal reflection takes place at the vertical face?
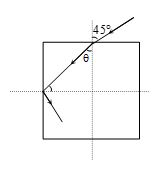
(a) \frac{{\sqrt{3}}}{2}
(b) \sqrt{{\frac{3}{2}}}
(c) \frac{3}{2}
(d) \frac{3}{{\sqrt{2}}}
Ans. (b)
Q.11
A spherical surface of radius of curvature R separates air (refractive index 1.0) from glass (refractive index 1.5). The centre of curvature is in the glass. A point object P placed in air is found to have a real image Q in the glass. The line PQ cuts the surface at a point O, and PO =OQ. The distance PO is equal to
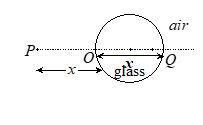
(a) 5R (b) 3R (c) 2R (d) 1.5R
Ans. (a)
Q.12
A ray of light passes through four transparent media with refractive indices m1, m2, m3 and m4 as shown in the figure. The surface of all media are parallel. If the emergent ray CD is parallel to the incident ray AB, then
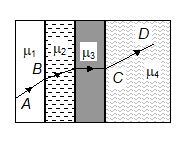
(a) m1 = m2 (b) m2 = m3 (c) m3 = m4 (d) m4 = m1
Ans. (d)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
Q.1
A plane mirror is placed at the bottom of a tank containing a liquid of refractive index . P is a small object at a height h above the mirror. An observer O, vertically above P, outside the liquid, observes P and its image in the mirror. The apparent distance between these two will be
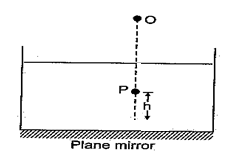
(a) \displaystyle 2\mu h
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{2h}}{\mu }
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{2h}}{{\mu -1}}
(d) \displaystyle h\left( {1+\frac{1}{\mu }} \right)
Ans (b)
Q.2
One side of a glass slab is silvered as shown. A ray of light is incident on the other side at angle of incidence \displaystyle i=45{}^\text{o}. Refractive index of glass is given as 1.5. The deviation of the ray of light from its initial path when it comes out of the slab is
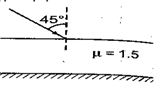
(a) 90º
(b) 180º
(c) 120º
(d) 45º
Ans (a)
Q.3
Consider the situation shown in figure. Water \displaystyle \left( {{{\mu }_{w}}=\frac{4}{3}} \right) is filled in a beaker upto a height of 10cm. A plane mirror is fixed at a height of 5 cm from the surface of water. Distance of image from the mirror after reflection from it of an object O at the bottom of the beaker is
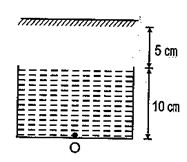
(a) 15 cm
(b) 12.5 cm
(c) 7.5 cm
(d) 10 cm
Ans (b)
Q.4
In the figure shown, \displaystyle {{\mu }_{1}}>{{\mu }_{2}}>{{\mu }_{3}}. What are the limits of angle i so that it is neither get total internal reflection at AB nor at CD ?
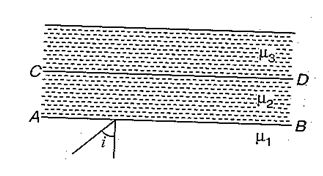
(a) \displaystyle \sin \,i\,<\,\frac{{{{\mu }_{2}}}}{{{{\mu }_{1}}}}
(b) \displaystyle \sin \,i\,<\,\frac{{{{\mu }_{3}}}}{{{{\mu }_{1}}}}
(c) \displaystyle \sin \,i\,<\,\frac{{{{\mu }_{3}}}}{{{{\mu }_{2}}}}
(d) None of these
Ans (b)
Q.5
A point object O is placed slightly above the centre C of a glass sphere as shown in figure. If it is viewed almost normally from above the sphere, its image is seen
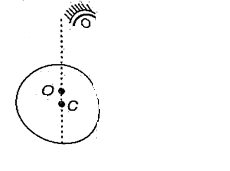
(a) at C
(b) above C
(c) below C
(d) may be above of below C
Ans (b)
Q.6
How much water should be filled in a container 21 cm in height so that it appears half filled when viewed from the top of the container?
(a) 8.0 cm (b) 10.5 cm (c) 12.0 cm (d) 14 cm
Ans. (d)
Q.7
If imj represents the refractive index when a ray of light goes from medium i to medium j, then the product 2m1 ´ 3m2 ´ 4m3 is equal to
(a) 3m1 (b) 3m2 (c) 1/1m4 (d) 1/4m2
Ans. (c)
Q.8
A ray of light from a denser medium strikes a rare medium at angle of incidence i. The reflected and the refracted rays make an angle of 90° with each other. The angles of reflection and refraction are r and r¢ respectively. The critical angle is
(a) sin–1 (tan r)
(b) sin–1 (cot i)
(c) sin–1 (tan r¢)
(d) sin–1 (sin i)
Ans. (a)
Q.9
A ray of light passes from vacuum into a medium of refractive index m. If the angle of incidence is twice the angle of refraction, then the angle of incidence is
(a) cos–1 (m/2)
(b) sin–1 (m/2)
(c) 2 cos–1 (m/2)
(d) 2 sin–1 (m/2)
Ans. (c)
Q.10
The critical angle of light going from medium A into medium B is q. The speed of light in medium A is v. The speed of light in medium B is
(a) \frac{v}{{\sin \theta }}
(b) v sin q
(c) \frac{v}{{\tan \theta }}
(d) v tan q
Ans. (a)
Q.11
A bird in air looks at a fish directly below it inside in a transparent liquid in a tank. If the distance of the fish as estimated by the bird is and that of the bird as estimated by the fish is , then the reactive index of liquid is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{{{h}_{2}}}}{{{{h}_{1}}}}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{{{h}_{1}}}}{{{{h}_{2}}}}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{{{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}}}{{{{h}_{1}}-{{h}_{2}}}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{{{{h}_{1}}-{{h}_{2}}}}{{{{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}}}
Ans. (a)
Q.12
A ray incident at an angle of incidence 60º enters a glass sphere of \displaystyle \mu =\sqrt{3}and it is reflected and refracted at the farther surface of the sphere. The angle between reflected and refracted rays at this surface is
(a) 120º (b) 90º (c) 60º (d) 150º
Ans. (b)
Q.13
Critical angle of glass is \displaystyle {{\theta }_{1}} and that of water is \displaystyle {{\theta }_{2}}. The critical angle for water and glass surface would be ( \displaystyle {{\mu }_{g}}=3/2,\,\,{{\mu }_{w}}=4/3)
(a) less than \displaystyle {{\theta }_{2}}
(b) between \displaystyle {{\theta }_{1}} and \displaystyle {{\theta }_{2}}
(c) greater than \displaystyle {{\theta }_{2}}
(d) less than \displaystyle {{\theta }_{1}}
Ans. (c)
Q.14
A 2 cm diameter coin rests flat on the bottom of a bowl in which the water is 20cm deep
( \displaystyle {{\mu }_{w}}=4/3). If the coin is viewed directly from above, what is its apparent diameter?
(a) 2 cm (b) 1.5 cm (c) 2.67 cm (d) 1.67 cm
Ans. (a)
15.
AB and CD are two slabs. The medium between the slabs has refractive index 2. Find the minimum angle of incidence at Q so that the ray is totally reflected by both the slabs.
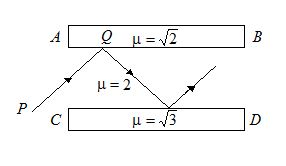
(a) 50o
(b) 90o
(c) 60o
(d) 30o
Ans (C)
16.
Figure shows a ray of light incident at an angle i on a glass slab of thickness t and refractive index m. Show that the lateral displacement, d, is given by
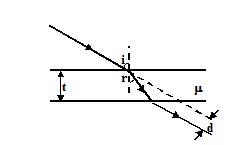
(a)t sin i \left( {1-\frac{{\cos i}}{{\sqrt{{{{\mu }^{2}}-{{{\sin }}^{3}}i}}}}} \left)
(b)t sin i \left( {1-\frac{{\sini}}{{\sqrt{{{{\mu }^{2}}-{{{\sin }}^{2}}i}}}}} \right)
(c)t sin i \left( {1-\frac{{\cos i}}{{\sqrt{{{{\mu }^{2}}-{{{\sin }}^{2}}i}}}}} \right)
(d)t sin i \left( {1-\frac{{\cos i}}{{\sqrt{{{{\mu }^{3}}-{{{\sin }}^{3}}i}}}}} \right)
Ans (c)
17.
A ray traveling in vacuum enters a long fiber of refractive index 1.5. At the curved surface the ray undergoes total internal reflection
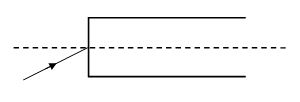
(a) for any angle of incidence.
(b) for angle of incidence between 15o and 45o
(c) for any angle of incidence between 0o and 30o
(d) for angle of incidence equal to 20o
Ans : (a)
18.
A glass cylinder of index m is surrounded by a sheath of index m¢. The surrounding medium has index m0. Show that the maximum angle q at which light will undergo total internal reflection is given by
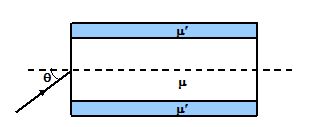
(a) \sqrt{{{{\mu }^{2}}-\mu {{‘}^{2}}}}
(b) \sqrt{{{{\mu }^{5}}-\mu {{‘}^{5}}}}
(c) \sqrt{{{{\mu }^{3}}-\mu {{‘}^{3}}}}
(d) \sqrt{{{{\mu }^{9}}-\mu {{‘}^{9}}}}
Ans (a)
19.
A hemispherical block of glass (m = 1.5) of radius 3 cm has a circular spot at its center. When viewed vertically from above, where is the image of the spot?
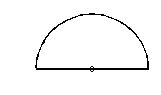
(a)at the centre
(b) in the right
(c) in the Left
(d) at the Mid
Ans (a)
Comprehension Based Question (20 and 21)
Locate the image of a small object produced by a glass sphere (n = 1.5) of radius 4 cm given that the object is located in air at
20
infinity
(a)3 cm from the centre.
(b)6 cm from the centre
(c)8 cm from the centre
(d)2 cm from the centre
Ans(b)
21.
20 cm from the centre of the sphere.
(a)8.50 cm from the centre
(b)8.57 cm from the centre
(c)8.65 cm from the centre
(d)8.00 cm from the centre
Ans(b)
