Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Basic Level)
Q.1
A simple harmonic motion is given by the equation x = 3 sin 3 p t + 4 cos 3 p t where x is in metres. The amplitude of the motion is
(a) 3 m (b) 4 m (c) 5 m (d) 7 m
Ans : (c)
Q.2
A particle is subjected to two mutually perpendicular SHM such that x = 2 sin wt and y = 2 sin [wt + (p/4). The path of the particle will be:
(a) An ellipse
(b) A straight line
(c) A parabola
(d) A circle
Ans. (a)
Q.3
Equation of a simple harmonic motion is given as
x = 3 sin 20pt + 4 cos 20 pt
where x is in cms and t in seconds. The amplitude is:
(a) 7 cm (b) 4 cm (c) 5 cm (d) 3 cm
Ans. (C)
Q.4
The composition of two simple harmonic motions of equal periods at right angle to each other and with a phase difference of p results in the displacement of the particle along
(a) circle (b) figure of eight (c) straight line (d) ellipse
Ans. (c)
Q.5
A particle is subjected to two mutually perpendicular simple harmonic motions such that its x and y coordinates are given by
\displaystyle \frac{{{{d}^{2}}}}{{2D\lambda }} The path of the particle will be
(a) a straight line (b) a circle (c) an ellipse (d) a parabola
Ans. (c)
Q.6
Two simple harmonic motions A and B are given respectively by the following equations
\displaystyle \frac{1}{{2\pi \sqrt{{LC}}}}
\displaystyle [{{M}^{0}}{{L}^{1}}{{T}^{{-1}}}]
The phase difference between the waves is
(a) \displaystyle [{{M}^{0}}{{L}^{0}}{{T}^{{-1}}}]
(b) \displaystyle [{{M}^{0}}{{L}^{0}}{{T}^{1}}]
(c) \displaystyle 2.5\times {{10}^{{-4}}}\text{cm}
(d) zero
Ans. (c)
Practice Questions (JEE Main Level)
Q.1
A point moves in the plane XY according to the law x = a sin wt and y = b cos wt, where a, b and w are positive constants. Find the trajectory equation y(x) of a point and the direction of its motion along this trajectory,
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{{{x}^{2}}}}{{{{a}^{2}}}}+\frac{{{{y}^{2}}}}{{{{b}^{2}}}}=1
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{{{x}^{2}}}}{{{{a}^{2}}}}-\frac{{{{y}^{2}}}}{{{{b}^{2}}}}=1
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{{{x}^{2}}}}{{{{a}^{2}}}}+\frac{{{{y}^{2}}}}{{{{b}^{2}}}}=2
(d) None
Ans : (a)
Q.2
The number of harmonic components in the oscillation represented by y = 4 cos2 2t sin 4t and their corresponding angular frequencies are:
(a) there; 2 rad/s, 4 rad/s, 8 rad/s
(b) two; 2 rad/s, 4 rad/s
(c) two;4 rad/s, 8 rad/s
(d) two; 2 rad/s, 8 rad/s
Ans. (c)
Q.3
A particle of mass m is attached to a spring (of spring constant k) and has a natural angular frequency w0. An external force F(t) proportional to cos wt (w ¹ w0) is applied to the oscillator. The time displacement of the oscillator will be proportional to:
(a) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}(\lambda /d)
(b) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}(\lambda /2d)
(c) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}(\lambda /3d)
(d) {{\sin }^{{-1}}}(\lambda /4d)
Ans. (b)
Q.4
When a damped harmonic oscillator completes 100 oscillations, its amplitude is reduced to 1/3 of its initial value. What will be its amplitude when it completes 200 oscillations:
(a) 1/5 (b) 2/3 (c) 1/6 (d) 1/9
Ans. (d)
Q.5
A particle, with restoring force proportional to displacemtn and resisting force proportional to velocity is subjected to a force F sin w If the amplitude of the particle is maximum for w = w1 and the energy of the particle is maximum for w = w2, then
(a) w1 = w0 and w2 ≠ w0
(b) w1 = w0 and w2 = w0
(c) w1 ≠ w0 and w2 = w0
(d) w1 ≠ w0 and w2 ≠ w0
Ans. (c)
Q.6
A point moves in the plane XY according to the law x = a sin wt and y = b cos wt, where a, b and w are positive constants the acceleration of the point as a function of its radius vector r relative to the origin of coordinates must be
(a) \displaystyle \vec{a}=\omega \vec{r}
(b) \displaystyle \vec{a}={{\omega }^{2}}\vec{r}
(c) \displaystyle \vec{a}=2{{\omega }^{2}}\vec{r}
(d) None
Ans :(b)
Q.7
Find the trajectory equation y(x) of a point if it moves according to the following laws
x = a sin wt and y = a sin 2 wt
(a) \displaystyle y=\frac{{2x\sqrt{{{{a}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}}}}}{a}
(b) \displaystyle y=\frac{{4x\sqrt{{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}}}{a}
(c) \displaystyle y=\frac{{2x\sqrt{{{{a}^{2}}-{{x}^{2}}}}}}{a}
(d) None
Ans : (c)
Q.8
The displacement equation of a particle is
x = 3 sin 2t + 4 cos 2t
The amplitude and maximum velocity will be respectively:
(a) 5, 10 (b) 3, 2 (c) 4, 2 (d) 3, 4
Ans. (a)
Q.9
Lissajous figure obtained by combining
x = a sin w t and \displaystyle \pi {{\cos }^{{1}}}\frac{4}{5}
will be:
(a) An ellipse (b) A straight line (c) A circle (d) A parabola
Ans. (a)
Q.10
The phase difference between the two simple harmonic oscillations
\displaystyle \frac{1}{2},\,\,\frac{1}{2} and \displaystyle \frac{1}{2},\,\,\frac{1}{2} is:
(a) \displaystyle \frac{1}{2},\,\,\frac{1}{2}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{1}{2},\,\,\frac{1}{2}
(c) \displaystyle A=\hat{i}+4\hat{j}2k\,\,and\,\,B=3\hat{i}5\hat{j}+k
(d) \displaystyle 4\hat{i}\hat{j}k
Ans. (c)
Practice Questions (JEE Advance Level)
1.
A uniform slender rod of length L and density s rotates about an axis through its end and perpendicular to the length width a constant angular velocity w. If the Young’s modulus of the rod is Y, find the elongation in the rod due to rotation (Neglect the effect of gravity).
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{\sigma \,{{L}^{3}}{{\omega }^{2}}}}{{3Y}}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{\sigma \,{{L}^{3}}{{\omega }^{4}}}}{{3Y}}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{\sigma \,{{L}^{3}}{{\omega }^{3}}}}{{5Y}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{{\sigma \,{{L}^{2}}{{\omega }^{3}}}}{{3Y}}
Ans (a)
2.
The resultant force acting on a particle executing SHM is 4 N when it is 5 cm away from the center of oscillation. Find the spring constant.
(a)50 N/m
(b)60 N/m
(c)80 N/m
(d)100 N/m
Ans (c)
3.
A block of mass 0.5 kg attached to a vertical spring extends it by 0.16m. It is pulled down a further 0.08m and released.
(a)
Write the equation for the displacement from equilibrium
(a)0.08 cos(7.83 t)m
(b)1.45 cos(5.36 t)m
(c)3.89 cos(2.53 t)m
(d)5.67cos(1.54 t)m
Ans (a)
(b)
Find the speed and acceleration when the spring extension is 0.1 m
(a)0.414 m/s, 1.25 m/s2
(b)0.414 m/s, 2.76 m/s2
(c)0.414 m/s, 3.68 m/s2
(d)0.414 m/s, 8.34 m/s2
Ans (c)
4.
The displacement of a block attached to a horizontal spring whose spring constant is 12 N/m is given by x = 0.2 cos(4t – 0.8) m. Find
(a)
the mass of the block
(a)0.5 kg
(b)0.75 kg
(c)2.6 kg
(d)3 kg
Ans (b)
(b)
the acceleration at t = 0.1 s
(a)-1.23 m/s2
(b)-0.46 m/s2
(c)-3.54 m/s2
(d)-2.95 m/s2
Ans (d)
5.
A 50 g block is attached to a vertical spring whose stiffness constant is 4 N/m. The block is released at the position where the spring is unextended.
(a)
What is the maximum extension of the spring
(a)0.14 m
(b)0.22 m
(c)0.245 m
(d)1.50 m
Ans (c)
(b)
How long does it take the block to reach the lowest point?
(a)0.3510s
(b)0.240s
(c)0.1760s
(d)1.576s
Ans (a)
6.
A block is resting on a piston which is moving vertically with a SHM of period 1.0 s. At what amplitude of motion will the block and piston separate? What is the maximum velocity of the piston at this amplitude?
(a)0.248 m, 0.39 m/s
(b)0.248 m, 2.06 m/s
(c)0.248 m, 3.39 m/s
(d)0.248 m, 1.56 m/s
Ans (d)
7.
A block attached to a spring oscillates with an amplitude of 10 cm and a period of 2.5 s. What is the period, if the following changes are made?
(a)
the amplitude is doubled
(a)No change
(b)Twice
(c) Thrice
Ans (a)
(b)
the mass is doubled
(a)0.25 s
(b)3.54 s
(c)5.65 s
(d)10.25 s
Ans (b)
(c)
the spring constant is doubled.
(a)1.00 s
(b)1.77 s
(c)1.87 s
(d)2.58 s
Ans (b)
8.
In an oscillating block-spring system the spring constant is 2.45 N/m, the amplitude is 16 cm, and the maximum speed is 56 cm/s. What is the mass of the block?
(a)0.2 kg
(b)0.5 kg
(c)1.4 kg
(d)2.8 kg
Ans (a)
9.
The 0.5 kg pan of a scale at a shop causes the vertical spring to extend by 14 cm. When a fish is placed in the pan, the system oscillates with a frequency 1.05 Hz. What is the mass of the fish?
(a)0.256 kg
(b)0.307 kg
(c)1.756 kg
(d)2.064 kg
Ans (b)
10.
In case of simple harmonic motion
(a)
what fraction of total energy is kinetic and what fraction is potential when displacement is one half of the amplitude.
(a)1/4
(b)1/2
(c)3/2
(d)5/8
Ans (a)
(b)
at what displacement the kinetic and potential energies are equal?
(a)A/ \sqrt{2}
(b)A/ \sqrt{5}
(c)A/ \sqrt{3}
(d)A/ \sqrt{6}
Ans (a)
11.
A particle executes SHM of amplitude A along the x-axis. At t = 0, the position of the particle is x = A/2 and it moves along the positive x-direction. Find the phase constant q if the equation is written as x = A sin (wt + q).
(a) 2π/6
(b) π/6
(c) 3π/7
(d) 4π/5
Ans (b)
12.
Two particles execute SHM of the same amplitude and frequency along the same straight line. They pass one another when going in opposite directions, each time their displacement is half of their amplitude. What is the phase difference between them?
(a)(2π/3)
(b)(π/3)
(c)(2π/5)
(d)(π/9)
Ans (a)
13.
A small particle slides inside a friction less spherical bowl of radius R, as shown in the figure. What is the period?
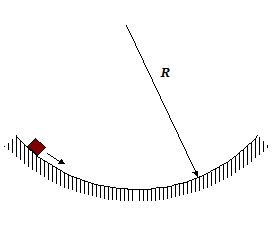
(a) 2\pi \sqrt{{\frac{R}{g}}}
(b) 5\pi \sqrt{{\frac{R}{g}}}
(c) 2\pi \sqrt{{\frac{R}{3g}}}
(d) 5\pi \sqrt{{\frac{R}{5g}}}
Ans (a)
14.
A solid cylinder of mass M and radius R is attached to a spring of stiffness k as shown in the figure. The cylinder can roll without slipping on a rough horizontal surface. Show that the centre of mass of the cylinder executes SHM and determine its time period.
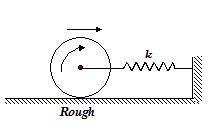
(a) 2\pi \sqrt{{\frac{{3M}}{{2k}}}}
(b) 3\pi \sqrt{{\frac{{M}}{{2k}}}}
(c) 2\pi \sqrt{{\frac{{2M}}{{3k}}}}
(d) 3\pi \sqrt{{\frac{{2M}}{{5k}}}}
Ans (a)
15.
A solid sphere of radius R is floating in a liquid of density r with half of its volume submerged. If the sphere is slightly pushed and released, it starts performing simple harmonic motion. Find the frequency of these oscillations.
(a) f=\frac{1}{{5\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{2g}}{{3R}}}}
(b) f=\frac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{5g}}{{3R}}}}
(c) f=\frac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{3g}}{{2R}}}}
(d) f=\frac{2}{{3\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{g}}{{2R}}}}
Ans (c)
