Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Principle of Superposition
In any medium, two or more waves can travel simultaneously without affecting the motion of each other. Therefore, at any instant the resultant displacement of each particle of the medium is merely the vector sum of displacements due to each wave separately. The principle is known as “principle of superposition”. It has been observed that when two sets of waves are made to cross each other, then after the waves have passed out of the region of crossing, they appear to have been entirely uninfluenced by the other set of waves. Amplitude, frequency and all other characteristics of the waves are as if they had crossed an undisturbed space.
As a simple example, we consider a long stretched string AB (see figure). The ends A and B of the string are made to vibrate up and down. Suppose the string is vibrating in the form of a triangular pulse, which propagates with a certain speed v.
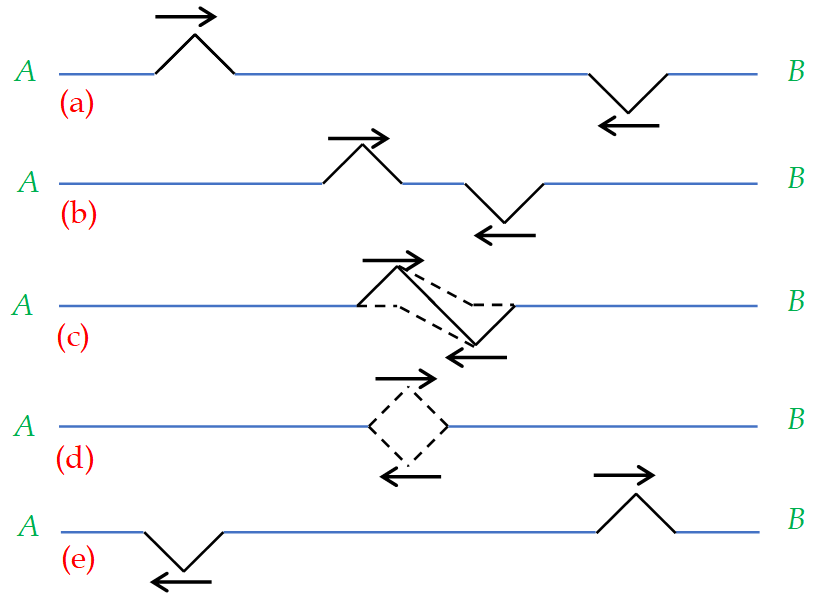
Figure (a) shows the position of pulse at t = 0. At a little later time, each pulse moves close to the outer as shown in figure (b), without any interference. Figure (c) represents the position at an instant when the two pulses interfere; the dashed curves represent the profile of the string, if each of the pulses were moving all by itself, whereas the solid curve shows the resultant
Displacement obtained by algebraic addition of each displacement. Shortly later in figure (d) the two pulses overlap each other and the resultant displacement is zero everywhere. At a much later time, the impulses cross each other (e) and move as if nothing had happened. This could hold provided the principle of superposition is true.
Interference
Superposition of Two Waves of Same Frequency and having Constant Phase Difference
Consider two waves of same frequency but having constant phase difference, say
\displaystyle \phi . Since they have same frequency, i.e. same angular frequency, we write
\displaystyle {{y}_{1}}={{a}_{1}}sin\omega t
and
\displaystyle {{y}_{2}}={{a}_{2}}sin\text{ }(\omega t+\phi )
where
\displaystyle {{a}_{1}} and \displaystyle {{a}_{2}} are two different amplitude, and \displaystyle \omega is common angular frequency of the two waves. By the principle of superposition, the resultant displacement is
\displaystyle y={{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}
\displaystyle ={{a}_{1}}sin\omega t+{{a}_{2}}sin\text{ }(\omega t+\phi )
\displaystyle ={{a}_{1}}\sin \omega t+{{a}_{2}}\sin \omega t\cos \phi +{{a}_{2}}\cos \omega t\sin \phi
\displaystyle =\text{ }sin\omega t({{a}_{1}}+{{a}_{2}}cos\phi )\text{ }+\text{ }cos\omega t({{a}_{2}}sin\phi )
Let us write
\displaystyle {{a}_{1}}+{{a}_{2}}cos\phi =Acos\theta … (i)
and \displaystyle {{a}_{2}}sin\phi =Asin\theta … (ii)
where A and \displaystyle \theta are new constants. This gives
\displaystyle y=\sin \omega tA\cos \theta +\cos \omega tA\sin \theta
or
\displaystyle y=A\sin (\omega t+\theta )
Hence the resultant displacement is simple harmonic and of amplitude A. Squaring and adding, equation (i) and (ii) we get
\displaystyle {{A}^{2}}{{\cos }^{2}}\theta +{{A}^{2}}{{\sin }^{2}}\theta ={{({{a}_{1}}+{{a}_{2}}\cos \phi )}^{2}}+{{({{a}_{2}}\sin \phi )}^{2}}
or,
\displaystyle {{A}^{2}}=a_{1}^{2}+a_{2}^{2}+2{{a}_{1}}{{a}_{2}}\cos \phi
hence finally resultant amplitude A can be written as
\displaystyle A=\sqrt{{a_{1}^{2}+a_{2}^{2}+2{{a}_{1}}{{a}_{2}}\cos \phi }}
We know that the intensity I is proportional to the square of the amplitude, i.e. \displaystyle I\propto {{a}^{2}}
hence resultant intensity is given can be written as
\displaystyle I={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}+2\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}}\cos \phi …(iii)
Thus, we find that the resultant intensity is not equal to the simple addition of the intensities due to separate waves.
Refer again to equation (iii), the intensity I is maximum when \displaystyle cos\phi =\text{ }+\text{ }1, that is, when phase difference is given by
\displaystyle \phi =\text{ }2n\pi (even multiple of \displaystyle \pi ).
Hence
\displaystyle {{I}_{{\max }}}={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}+2\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}}
\displaystyle \Rightarrow \text{ }{{I}_{{\max }}}={{\left( {\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}}}+\sqrt{{{{I}_{2}}}}} \right)}^{2}}
A point where the resultant intensity becomes maximum a constructive interference is said to take place. At these points the waves superimpose in the way shown in the figure.
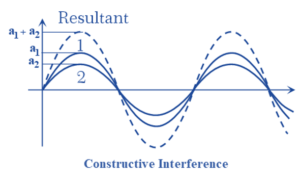
The resultant intensity is, thus, greater than the simple addition of the two separate intensities. And if
\displaystyle {{I}_{1}}={{I}_{2}}=I\text{ }\ \text{then}\ \text{ }{{I}_{{\max }}}=4I
The resultant intensity I is minimum when
\displaystyle cos\phi =\text{ }-\text{ }1, i.e., when \displaystyle \phi is given by odd multiple of \displaystyle \pi
Hence
\displaystyle \phi =(2n+1)\pi .
therefore,
\displaystyle {{I}_{{\min }}}={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}-2\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}}
\displaystyle \Rightarrow \text{ }{{I}_{{\min }}}={{\left( {\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}}}-\sqrt{{{{I}_{2}}}}} \right)}^{2}}
A point where the resultant intensity becomes minimum a destructive interference is said to take place. At these points the waves superimpose in the way shown in the figure.
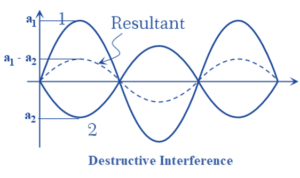
The resultant intensity is thus less than the sum of two separate intensities. And if \displaystyle {{I}_{1}}={{I}_{2}}=I then \displaystyle {{I}_{{min}}}~=~0, which means that there is no light.
As we discussed above the resultant intensity of two interfering waves is given by
\displaystyle {{I}_{R}}={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}+2\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}}\cos \phi
Spl.case : For two waves of same intensity `I’ and having a constant phase difference of \displaystyle \phi , the resultant intensity is given by
\displaystyle {{I}_{R}}=2I+2I\cos \phi
\displaystyle (\because \ \ {{I}_{1}}={{I}_{2}}=I)
\displaystyle =2I(1+\cos \phi )
\displaystyle hence\text{ }{{I}_{R}}=4I{{\cos }^{2}}\frac{\phi }{2}
Therefore, we find that when two waves of the same frequency travel in approximately the same direction and have a phase difference that remains constant with the passage of time, the resultant intensity of light in not distributed uniformly in space means we do not get a uniform light in space.(Here for better understanding the space can be considered as a screen )The non-uniform distribution of the light intensity due to the superposition of two waves is called interference.
At some points in the space or screen where the phase difference \displaystyle \phi is equal to \displaystyle 2n\pi the intensity becomes maximum and the interference at these points is called constructive interference. At some other points in the space or screen where the phase difference \displaystyle \phi is equal to \displaystyle \left( {2n+1} \right)\pi the intensity is minimum and the interference at these points is called destructive interference.
The average intensity on the screen is exactly what should exist in the absence of interference. Means there is no net loss or gain of energy but there is a redistribution of energy during interference.
Illustration
Two waves of same frequency but of amplitudes a and 2a respectively superimpose over each other. What is the amplitude at a point where the phase difference is \displaystyle \frac{{3\pi }}{2}?
Solution
Here
\displaystyle a\,\,=\,\,\sqrt{{a_{1}^{2}+a_{2}^{2}\,\,+\,\,2{{a}_{1}}\,\,{{a}_{2}}\,\,\,\cos \,\,\phi }}
\displaystyle =\,\,\,\sqrt{{{{a}^{2}}\,\,+\,\,{{{(2a)}}^{2}}+2a\,\,\cdot \,\,2a\,\cdot \,\,\cos \,\,\frac{{3\pi }}{2}}}
= \displaystyle \sqrt{{{{a}^{2}}+4{{a}^{2}}+4{{a}^{2}}\times \,\,0}}
= \displaystyle \sqrt{{5\,\,{{a}^{2}}}}
= \displaystyle \sqrt{5}\,\,a
Illustration
Two coherent sound sources are at distances \displaystyle {{x}_{1}}= 0.2 m and \displaystyle {{x}_{2}}= 0.48 m from a point. Calculate the intensity of the resultant wave at that point if the frequency of each wave is 400 Hz and velocity of wave in the medium is v = 448 m/s. The intensity of each wave is \displaystyle {{I}_{o}} = 60 \displaystyle W/{{m}^{2}}?
Solution
Path difference,
\displaystyle \Delta x={{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}
\displaystyle =0.48-0.2=0.28m
we know that phase difference is given by
\displaystyle \phi =\frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }\Delta x
\displaystyle =\left( {\frac{{2\pi }}{{c/\nu }}} \right)\Delta x
\displaystyle =\frac{{2\pi \left( {400} \right)\left( {0.28} \right)}}{{448}}
\displaystyle =\frac{\pi }{2}
Since
\displaystyle I={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}+2\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}}\cos \phi
therefore
\displaystyle I={{I}_{o}}+{{I}_{o}}+2{{I}_{o}}\cos \left( {\pi /2} \right)
\displaystyle =2{{I}_{o}}=2\left( {60} \right)=120\text{ }W/{{m}^{2}}
Illustration
Consider interference due to two coherent waves of same frequency and constant phase difference having intensities I and 4I, respectively. What is the resultant intensity when the phase difference between these two waves is \displaystyle \pi /2and \displaystyle \pi ?
Solution
According to Eq.
\displaystyle I={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}+2\sqrt{{{{I}_{1}}{{I}_{2}}}}\cos \delta
Given : \displaystyle {{I}_{1}}= I and \displaystyle {{I}_{2}}= 4I, so
I = 5 I + 2 I \displaystyle \sqrt{4}\ \cos \delta
= 5 I + 4 I \displaystyle \cos \delta
Hence
\displaystyle {{I}_{{\pi /2}}}=5I+4I\cos 90{}^\circ =5I
\displaystyle {{I}_{{\pi /2}}}=5I+4I\cos 90{}^\circ =5I
\displaystyle {{I}_{\pi }}=\text{ }5I+\text{ }4Icos\pi =I
Illustration
Two point sources X and Y emit waves of same frequency and speed but Y lags in phase behind X by \displaystyle 2\pi l radian. Find the distance XO using n as an integer If there is a maximum in direction D .
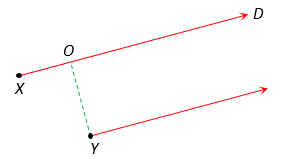
Solution
Using concept of wave that a distance \displaystyle \lambda is equivalent to a phase of \displaystyle 2\pi . So at D if \displaystyle {{\phi }_{x}} is the phase of wave from source X and \displaystyle {{\phi }_{y}} is the phase of wave from Y then their phase difference at D is \displaystyle \Delta \phi =\text{ }{{\phi }_{x}}-{{\phi }_{y}}. This phase difference is produced because the waves have travelled different distance from their sources to some point D in space
Where \displaystyle {{\phi }_{x}} .can be calculated as follows
a distance of \displaystyle \lambda is equivalent to a phase \displaystyle 2\pi
so a distance XO + OD is equivalent to a phase = \displaystyle \frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(XO+OD) {see the diagram}
this is the phase of wave reaching at D from the source X hence \displaystyle {{\phi }_{x}} = \displaystyle \frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(XO+OD)
similarly \displaystyle {{\phi }_{y}} = \displaystyle \frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(YD)
but YD = OD so
\displaystyle {{\phi }_{y}} = \displaystyle \frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(OD)
Hence total phase difference at D is given by
\displaystyle \Delta \phi =({{\phi }_{x}}-{{\phi }_{y}})-2\pi l
( extra phase difference \displaystyle 2\pi l is given in the question that source Y is lagging behind source X by \displaystyle 2\pi l )
so
\displaystyle \Delta \phi =\frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(XO+OD)-\frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(OD)-2\pi l
\displaystyle \Rightarrow \text{ }\Delta \phi =\frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(XO)-2\pi l
For maximum or constructive interference at D phase difference \displaystyle \Delta \phi should be equal to \displaystyle 2n\pi .
Hence \displaystyle \text{2n}\pi =\frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }(XO)-2\pi l
or \displaystyle XO=(n+l)\lambda
Illustration
A system consists of two coherent point sources 1 and 2 located in a certain plane. The sources are separated by a distance d and the wavelength of radiation is \displaystyle \lambda . Taking into account that the oscillations of source 2 lag in phase behind the oscillations of source 1 by \displaystyle \phi \displaystyle (\phi <\pi ), find the angle \displaystyle \theta at which the radiation intensity is maximum
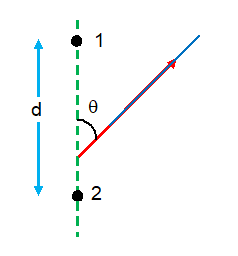
Solution
Path difference at angle \displaystyle \theta is
\displaystyle \Delta x\text{ }=\text{ }d\text{ }sin\text{ }(90\text{ }-\theta )\text{ }=\text{ }d\text{ }cos\theta
corresponding phase difference between 1 and 2 is
\displaystyle \phi = \displaystyle \left( {\frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }} \right) \displaystyle \Delta x
\displaystyle \phi ‘ = \displaystyle \left( {\frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }} \right) d \displaystyle cos\theta
so net phase difference will be
\displaystyle {{\phi }_{{net}}}=\text{ }\phi -\phi ‘
= \displaystyle \frac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }d \displaystyle cos(\theta +\phi )
for maximum intensity
\displaystyle {{\phi }_{{net}}}=2n\pi
\displaystyle [where n\text{ }=\text{ }0,\pm 1,\pm 2\text{ }\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots ]
hence
\displaystyle \theta ={{\cos }^{{-1}}} \displaystyle \left[ {\frac{\lambda }{{2\pi d}}\left( {2n\pi -\phi } \right)} \right]
or \displaystyle \theta ={{\cos }^{{-1}}} \displaystyle \left[ {\frac{\lambda }{d}\left( {n-\frac{\phi }{{2\pi }}} \right)} \right]
Practice Questions (Basic Level)
1.
Two coherent sources of light can be obtained by
(a) Two different lamps
(b) Two different lamps but of the same power
(c) Two different lamps of same power and having the same colour
(d) None of the above
Ans (d)
2.
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of intensities I and 4I are superposed. The maximum and minimum possible intensities in the resulting beam are
(a) 5I and I
(b) 5I and 3I
(c) 9I and I
(d) 9I and 3I
Ans (c)
3.
If the ratio of intensities of two waves is 1 : 25, then the ratio of their amplitudes will be
(a) 1 : 25
(b) 5 : 1
(c) 26 : 24
(d) 1 : 5
Ans (d)
4.
Two identical light sources S1 and S2 emit light of same wavelength λ. These light rays will exhibit interference if
(a) Their phase differences remain constant
(b) Their phases are distributed randomly
(c) Their light intensities remain constant
(d) Their light intensities change randomly
Ans (a)
5.
If two waves represented by {{y}_{1}}=4\sin \omega t and {{y}_{2}}=3\sin \left( {\omega t+\frac{\pi }{3}} \right) interfere at a point, the amplitude of the resulting wave will be about
(a) 7
(b) 6
(c) 5
(d) 3.5
Ans (b)
6.
If the ratio of amplitude of two waves is 4 : 3, then the ratio of maximum and minimum intensity is
(a) 16 : 18
(b) 18 : 16
(c) 49 : 1
(d) 94 : 1
Ans (c)
7.
Coherent sources are those sources for which
(a) Phase difference remain constant
(b) Frequency remains constant
(c) Both phase difference and frequency remains constant
(d) None of these
Ans (c)
8.
Two waves are represented by the equations {{y}_{1}}=a\sin \omega t and {{y}_{2}}=a\cos \omega t. The first wave
(a) Leads the second by π
(b) Lags the second by π
(c) Leads the second by \frac{\pi }{2}
(d) Lags the second by \frac{\pi }{2}
Ans (d)
9.
Four coherent waves are represented by
(i) y = a1 sinw t
(ii) y={{a}_{2}}\sin (\omega \,t+\varphi )
(iii) y={{a}_{1}}\sin 2\omega \,t
(iv) y={{a}_{2}}\sin 2(\,\omega \,t+\varphi )
Interference may be observed due to superposition of
(a) (i) and (ii) & (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (iii) only
(c) (ii) and (iv) only
(d) (i) and (ii) & (iii) and (iv)
Ans : (d)
10.
Young’s experiment establishes that
(a) Light consists of waves
(b) Light consists of particles
(c) Light consists of neither particles nor waves
(d) Light consists of both particles and waves
Ans (a)
11.
In the interference pattern, energy is
(a) Created at the position of maxima
(b) Destroyed at the position of minima
(c) Conserved but is redistributed
(d) None of the above
Ans (c)
12.
Monochromatic green light of wavelength 5\times {{10}^{{-7}}}milluminates a pair of slits 1 mm The separation of bright lines on the interference pattern formed on a screen 2 m away is
(a) 0.25 mm
(b) 0.1 mm
(c) 1.0 mm
(d) 0.01 mm
Ans (c)
13.
The figure shows a double slit experiment P and Q are the slits. The path lengths PX and QX are n\lambda and (n+2)\lambda respectively, where n is a whole number and l is the wavelength. Taking the central fringe as zero, what is formed at X
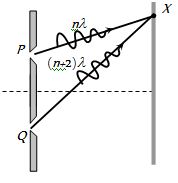
(a) First bright
(b) First dark
(c) Second bright
(d) Second dark
Ans (c)
14.
In Young’s double slit experiment, a glass plate is placed before a slit which absorbs half the intensity of light. Under this case
(a) The brightness of fringes decreases
(b) The fringe width decreases
(c) No fringes will be observed
(d) The bright fringes become fainter and the dark fringes have finite light intensity
Ans (d)
15.
In Young’s experiment, the distance between the slits is reduced to half and the distance between the slit and screen is doubled, then the fringe width
(a) Will not change
(b) Will become half
(c) Will be doubled
(d) Will become four times
Ans (d)
16.
The Young’s experiment is performed with the lights of blue (l = 4360 Å) and green colour (l = 5460 Å), If the distance of the 4th fringe from the centre is x, then
(a) x (Blue) = x (Green)
(b) x (Blue)> x (Green)
(c) x (Blue) < x (Green)
(d) \frac{{x(Blue)}}{{x(Green)}}=\frac{{5460}}{{4360}}
Ans (c)
17.
In Young’s experiment, light of wavelength 4000 Å is used to produce bright fringes of width 0.6 mm, at a distance of 2 meters. If the whole apparatus is dipped in a liquid of refractive index 1.5, then fringe width will be
(a) 0.2 mm
(b) 0.3 mm
(c) 0.4 mm
(d) 1.2 mm
Ans (c)
18.
In a Young’s double slit experiment, the fringe width will remain same, if (D = distance between screen and plane of slits, d = separation between two slits and l = wavelength of light used) (a) Both l and D are doubled
(b) Both d and D are doubled
(c) D is doubled but d is halved
(d) l is doubled but d is halved
Ans (b)
19.
In Young’s double slit experiment, angular width of fringes is 0.20o for sodium light of wavelength 5890 Å. If complete system is dipped in water, then angular width of fringes becomes
(a) 0.11o
(b) 0.15o
(c) 0.22o
(d) 0.30
Ans (b)
20.
In Young’s double slit experiment, the distance between the slits is 1 mm and that between slit and screen is 1 meter and 10th fringe is 5 mm away from the central bright fringe, then wavelength of light used will be
(a) 5000 Å
(b) 6000 Å
(c) 7000 Å
(d) 8000 Å
Ans (a)
21.
In Young’s double slit experiment, a mica slit of thickness t and refractive index m is introduced in the ray from the first source S1. By how much distance the fringes pattern will be displaced
(a) \frac{d}{D}(\mu -1)\ t
(b) \frac{D}{d}(\mu -1)\ t
(c) \frac{d}{{(\mu -1)D}}
(d) \frac{D}{d}(\mu -1)
Ans (b)
22.
If a white light is used in Young’s double slit experiments then a very large number of coloured fringes can be seen
(a) With first order violet fringes being closer to the central white fringes
(b) First order red fringes being closer to the central white fringes
(c) With a central white fringe
(d) With a central black fringe
Ans (c)
23.
In a Young’s double slit experiment, 12 fringes are observed to be formed in a certain segment of the screen when light of wavelength 600 nm is used. If the wavelength of light is changed to 400 nm, number of fringes observed in the same segment of the screen is given by
(a) 12
(b) 18
(c) 24
(d) 30
Ans (b)
24.
In Young’s double slit experiment, distance between two sources is 0.1 mm. The distance of screen from the sources is 20 cm. Wavelength of light used is 5460 Å. Then angular position of the first dark fringe is
(a) 0.08°
(b) 0.16°
(c) 0.20°
(d) 0.313°
Ans (d)
Practice Questions (JEE Main Level)
1.
Two speakers are 1 m apart and emit sound of frequency 1000 Hz in phase. A listener walks along a line that is parallel to the line joining the speakers and 8 m away from their midpoint. What is the separation between the central maximum and the first minimum in loudness? Take the speed of sound to be 340 m/s.
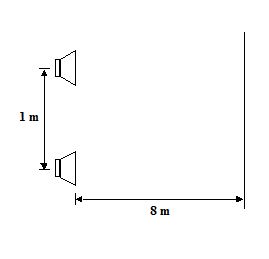
(a)2.00 m
(b) 1.50 m
(c) 1.36 m
(d) 1.00 m
Ans (c)
Practice Questions (JEE Advance Level)
1.
For the arrangement of two speakers shown in figure, assume S1 is p rad out of phase with S2. The frequency is 500 Hz. What is the minimum value of d for which the intensity at P is a maximum? Take the speed of sound to be 340 m/s.
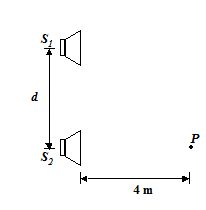
(a) 1.00 m
(b) 1.25 m
(c) 1.50 m
(d) 1.68 m
Ans (d)
