Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
1.
A semiconductor has the electron concentration 0.45 × 1012 m–3 and hole concentration 5 × 1020 m–3. Find its conductivity. Given: electron mobility = 0.135 m2V–1s–1 and hole mobility = 0.048 m2v–1s–1; e = 1.6 × 10–19 coulomb.
(a) 1.548 \displaystyle \Omega m–1
(b) 1.224 \displaystyle \Omega m–1
(c) 3.845 \displaystyle \Omega m–1
(d) 0.456 \displaystyle \Omega m–1
Ans (c)
2.
When the voltage drop across a p–n junction diode is increased from 0.70V to 0.71 V, the change in the diode current is 10 mA. What is the dynamic resistance of the hole?
(a) 27 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 20 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) 4 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 1 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans (d)
3.
In a p type semiconductor the acceptor level is situated 57 meV above the valence band. The maximum wavelength of light required to produce a hole will be
(a) 57 × 10–3Å
(b) 11.61 × 10–33 watt
(c) 57 Å
(d) 217100 Å.
Ans (d)
4.
The band of maximum energy in which electrons are present is called
(a) valence band
(b) forbidden band
(c) conduction band
(d) fermi band.
Ans (a)
5.
The relation between the number of free electrons in semiconductors (n) and its temperature (T) is
(a) n \displaystyle \propto T
(b) n\propto \sqrt{T}
(c) n \displaystyle \propto T3/2
(d) n \displaystyle \propto T2.
Ans (c)
6.
The electron mobility in an n type germanium is 3900 cm2/V-s and its conductivity is 6.24 mho cm–1, then the impurity concentration will be
(a) 1016/cm3
(b) 1015/cm3
(c) 1013/cm
(d) 1012/cm3.
Ans (a)
7.
Polymers are the substance which are
(a) amorphous in nature
(b) semi-solids
(c) crystalline in nature
(d) none of these.
Ans (d)
8.
In which case is the junction diode forward biased
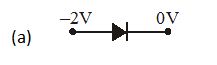
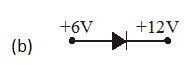
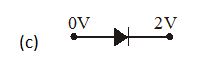
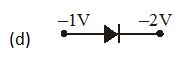
Ans (d)
9.
Acceptor type or p type semiconductor is formed by adding impurity of valency
(a) 6
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 3.
Ans(d)
10.
The ripple factor in a full-wave rectifier is
(1) 0.48
(2) 1.21
(3) 0.62
(4) 1.0.
Ans (a)
11.
Assuming that the junction diode is ideal, the current in arrangement as shown in figure is
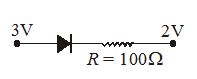
(a) 2 mA
(b) 10 mA
(c) 20 mA
(d) 30 mA.
Ans (b)
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Get Full Access Of the Chapters
