Video Lecture
Theory For Notes Making
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Objective Assignment
Q.1
The reactance of a 25 µF capacitor at the AC frequency of 4000 Hz is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{5}{\pi }\Omega
(b) \displaystyle \sqrt{{\frac{5}{\pi }}}\Omega
(c) \displaystyle 10\,\Omega
(d) \displaystyle \sqrt{{10}}\,\Omega
Ans. (a)
Q.2
What will be the approximate resistance offered by a capacitor of 10 µF and frequency 100 Hz ?
(a) 160 Ω (b) 1600 Ω (c) 16 Ω (d) None of the above
Ans. (a)
Q.3
An AC voltage is applied to a resistance R and an inductor L in series. If R and the inductive reactance are both equal to 3Ω, the phase difference between the applied voltage and the current in the circuit is
(a) π / 4 (b) π / 2 (c) zero (d) π / 6
Ans. (a)
Q.4
The power factor of an R–L circuit is \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{2}}}. If the frequency of AC is doubled, what will be the power factor ?
(a) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{3}}}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{5}}}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{7}}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{{11}}}}
Ans. (b)
Q.5
An inductive coil has a resistance of 100 Ω. When an AC signal of frequency 1000 Hz is applied to the coil, the voltage leads the current by 45º. The inductance of the coil is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{10\pi }}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{20\pi }}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{40\pi }}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{60\pi }}
Ans. (b)
Q.6
Two coils have a mutual inductance 0.005 H. The current changes in the first coil according to equation \displaystyle I={{I}_{0}}\,\sin \,\omega t, where \displaystyle {{I}_{0}}=10A and \displaystyle \omega =100\pi \,rad/s. The maximum value of emf in the second coil is (in volt).
(a) 2 \displaystyle \pi
(b) 5 \displaystyle \pi
(c) \displaystyle \pi
(d) 4 \displaystyle \pi
Ans. (b)
Q.7
In an AC circuit, V and I are given by V = 150 sin (150 t) volt and \displaystyle I=150\sin \left( {150\,t+\frac{\pi }{3}} \right) The power dissipated in the circuit is
(a) 106 W (b) 150 W (c) 5625 W (d) zero
Ans. (c)
Q.8
In an AC circuit an alternating voltage \displaystyle e=200\sqrt{2}\sin 100\,tvolt is connected to a capacitor of capacity 1µF. The rms value of the current in the circuit is
(a) 100 mA (b) 200 mA (c) 20 mA (d) 10 mA
Ans. (c)
Q.9
An AC voltage is applied to a resistance R and an inductor L in series. If R and the inductive reactance are both equal to 3Ω, the phase difference between the applied voltage and the current in the circuit is
(a) π/4 (b) π/2 (c) zero (d) π/6
Ans. (a)
Q.10
In the case of an inductor
(a) voltage lags the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}
(b) voltage leads the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}
(c) voltage leads the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{3}
(d) voltage leads the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{4}
Ans. (b)
Q.11
The inductive time constant in an electrical circuit is
(a) \displaystyle L\,R
(b) \displaystyle \frac{L}{R}
(c) \displaystyle \sqrt{{\frac{L}{R}}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{R}{L}
Ans. (b)
Q.12
In an AC circuit, V and i are given by V = 100 sin (100 t) volt and \displaystyle i=100\sin \left( {100\,t+\frac{\pi }{3}} \right)amp The power dissipated in the circuit is
(a) 104 W (b) 2.5 kW (c) 5 kW (d) 5 W
Ans. (b)
Q.13
The reactance of 25 µF capacitor at the AC frequency of 4000 Hz is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{5}{\pi }Ω
(b) \displaystyle \sqrt{{\frac{5}{\pi }}}Ω
(c) 10 Ω
(d) \displaystyle \sqrt{{10}}Ω
Ans. (a)
Q.14
The frequency for which a 5 µF capacitor has a reactance of \displaystyle \frac{1}{{1000}}Ω is given by
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{100}}{\pi }MHz
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{1000}}{\pi }Hz
(c) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{1000}}Hz
(d) 1000 Hz
Ans. (a)
Q.15
The capacity of a pure capacitor is 1 F. In DC circuits, its effective resistance will be
(a) zero (b) infinite (c) 1 Ω (d) 1/2 Ω
Ans. (b)
Q.16
The rms voltage of the wave form shown is
(a) 10 V
(b) 7 V
(c) 6.37 V
(d) None of these
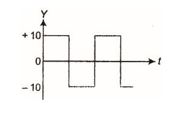
Ans. (a)
Q.17
The output sinusoidal current versus time curve of a rectifier is shown in the figure. The average value of output current in this case is
(a) 0
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{2}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{2{{I}_{0}}}}{\pi }
(d) \displaystyle {{I}_{0}}
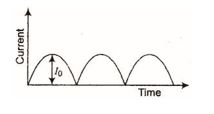
Ans. (c)
18.
The capacitor reactance of a capacitor in d.c. circuit in ohms is
(A) \frac{1}{{\omega C}}
(B) \displaystyle \omega C
(C) zero
(D) \displaystyle \infty
Ans (A)
19.
The reactance of a inductor at 50 Hz is 10 \displaystyle \Omega . What will be its reactance at 200 Hz ?
(A) 10 \displaystyle \Omega
(B) 40 \displaystyle \Omega
(C) 2.5 \displaystyle \Omega
(D) 20 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans (B)
20.
An inductive circuit contains a resistance of 10 \displaystyle \Omega and inductance of 2H. If an a.c. voltage of 120 V and frequency 60 Hz is applied to this circuit, the current in circuit would be nearly
(A) 0.32 A
(B) 0.16 A
(C) 0.48 A
(D) 0.80 A
Ans (B)
21.
What is the average value of a.c. over a half cycle
(A) zero
(B) \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{\pi }
(C) \displaystyle \frac{{2{{I}_{0}}}}{\pi }
(D) none of these
Ans (C)
22.
In an AC circuit having R and L in serries
(A) voltage leads current
(B) current leads voltage
(C) voltage and current are increase
(D) voltage and current are in opposite phase
Ans (A)
23.
Average power in a pure inductive circuit is
(A) irms´ vrms
(B) 2 irms´ vrms
(C) 1
(D) zero
Ans (D)
24.
The root mean square value of voltage (V) in an AC circuit is
(A) 0.637Vmax
(B) 0.707 Vmax
(C) 2Vmax
(D) \sqrt{2}Vmax
Ans (B)
25.
In an AC series circuit, instantaneous voltage is maximum while instantaneous current is zero. The source is connected to
(A) pure inductor only
(B) pure resistance only
(C) pure capacitor only
(D) (A) or (C)
Ans (D)
26.
In the circuit shown, the voltage in C & L are
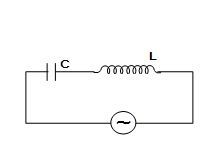
(A) out of phase by \displaystyle \pi
(B) out of phase by \displaystyle \pi /2
(C) out of phase by \displaystyle \pi /4
(D) In Phase
Ans (A)
27.
If the mean value of an alternating voltage is \frac{{28\sqrt{2}}}{\pi } volt, its rms value is
(A) 28 volt
(B) 14 volt
(C) 14 \sqrt{2} volt
(D)zero
Ans (B)
28.
When an alternating voltage source is connected to a pure inductor, the difference between phase of instantaneous current through the inductor and the phase of instantaneous potential difference across the inductor at t = T/4 sec. is
(A)zero
(B) \displaystyle \pi /2 rad.
(C) – \displaystyle \pi /2 rad.
(D) \displaystyle \pi /4 rad.
Ans (C)
Subjective Assignment
Q.1
What do you understand by peak value and rms value of alternating current ? Derive a relation between them.
Q.2
When an ac source is connected across an ideal inductor, show on a graph the nature of variation of the voltage and the current over one complete cycle.
Q.3
Sketch the graph to show how the reactance of (i) a capacitor (ii) an inductor varies as a function of frequency?
Q.4
Why do we prefer a choke coil to a rheostat in controlling a.c.?
Q.5
Obtain the formula for the ‘power loss’ in a conductor of resistance R, carrying a current I.
Q.6
Alternating current through pure inductor and pure capacitor is wattles. Why?
Q.7
A capacitor blocks d.c. and allows a.c.. Why?
Q.8
An ac voltage, \displaystyle E={{E}_{0}}\,\sin \,\omega t is applied across an inductor L. Obtain an expression for the current.
Q.9
Prove that an ideal capacitor, in an a.c. circuit does not dissipate power.
Q.10
An a.c. current, \displaystyle I\,=\,{{I}_{0}} sin \displaystyle I\,=\,{{I}_{0}}\,\sin \,\,\,\omega t\,, produces a certain heat, H, in a resistor R, over a time \displaystyle T\,=\,2\pi /\omega . Write the value of the d.c. current that would produce the same heat, in the same resis \displaystyle T\,=\,2\pi /\omega tor, in the same time.
Q.11
Find the time taken by 60Hz a.c. to reach its peak value from zero.
Q.12
220 volt a.c. is more dangerous than 220 volt d.c. why?
Q.13
The d.c. and a.c. both, can be measured by a hot wire instrument. Why?
Q.14
An alternating voltage given by V=70 sin 100 \displaystyle \pi t is connected across a pure resistor of 25 \displaystyle \Omega . Find (i) the frequency of the source. (ii) the rms current through the resistor.
Q.15
What is meant by rms value of a.c.? Derive an expression for alternating emf?
Q.16
What do you understand by peak value and rms value of alternating current ? Derive a relation between them.
Q.17
The instantaneous current from an a.c source is given by I=5 sin 314 t. What is the rms value of the current? Also find the first time after t=0 at which the current reaches the rms value
Ans. 3.54 A, 1/400 sec
Q.18
If the effective current in a 50 cycle a.c circuit is 5 A, what is the peak value of current? What is the current 1/600 sec. after it was zero?
Ans. 7.07 A, 3.535 A
Q.19
The electric mains in a house are marked 220 V, 50 hz. Write down the equation for instantaneous voltage.
Ans. 311 sin 100 pt
Q.20
The equation of an alternating current is i=4 cos (100 pt-q) ampere. Calculate the peak value and frequency of a.c.
Ans. 4 amp., 50 hz
Q.21
Write general equation for instantaneous e.m.f of a 60 cycle generator, whose peak voltage is 180 volt.
Ans. E=180 sin 120 pt or E=180 cos 120pt
Q.22
The effective value of current in a 50 cycle a.c. circuit is 5.0 A. What is the value of current (1/300)s after it is zero?
Ans. 6.12 A
Q.23
The instantaneous value of an alt. voltage is given by E=140 sin 300 t. What is (i) peak value of voltage (ii) the r.m.s value (iii) frequency of supply?
Ans. 140 V, 99 V, 47.7 Hz
Q.24
The electric current in a circuit is given by i=i0 (t/t) for some time. Calculate the r.m.s current for the period t=0 to t=t.
Ans. i0/Ö3
Q.25
A resistance of 20 W is connected to a source of alternating current rated 110 V, 50 Hz. Find (a) the r.m.s current, (b) the maximum instantaneous current in the resistor and (c) the time taken by the current to change from its maximum value to the r.m.s value.
Ans. 5.5 A, 7.8 A, 2.5´10-3 s
Q.26
A sinusoidal voltage V=200 sin 314 t is applied to a resistor of 10 ohm. Calculate (i) r.m.s value of voltage (ii) r.m.s value of current (iii) power dissipated as heat in watt.
Ans. 141.4 V, 14.14 A, 1999.3 W
Q.27
A pure inductor of self inductance 1 H is connected across and alternating voltage of 115 V and frequency 60 Hz. Calculate the (i) inductive reactance (ii) effective current (iii) peak current (iv) average power consumed.
Ans. 377.1 W, 0.3 A, 0.43 A, Zero
Q.28
How much inductance should bc connected to 200 V, 50 c/s supply so that a maximum current of 0.5 A flows through it?
Ans. 1.79 H
Q.29
Alternating e.m.f of E=220 sin 100 pt is applied to a circuit containing an inductance of (1/p) henry. Write equation for instantaneous current through the circuit. What will be the reading of a.c. galvanometer connected in the circuit?
Ans. I=2.2 sin (100 pt-zp/2), 1.555 A
Q.30
A 3mF capacitor is connected to a 220 V, 50 hz a.c. source. Calcutale the rms value of current through the circuit. Also, find the peak value of voltage across the capacitor.
Ans. 0.207 A, 311.1 V
Q.31
A 60 mF capacitor is connected to a 110 V, 60 Hz a.c. supply. Determine the r.m.s value of current in the circuit.
Ans. 2.49 A
Q.32
A capacitor of 10 mF is connected to an a.c source of e.m.f E=220 sin 100 pt. Write the equation of instantaneous current through the circuit. What will be the reading of a.c. ammeter connected in the circuit?
Ans. I=0.691 sin (100 pt + p/2), 0.489 A
