Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Buoyancy and archimede’s principle
If an object is immersed in or floating on the surface of, a liquid, it experiences a net vertically upward force due to liquid pressure. This force is called as Buoyant force or force of Buoyancy and it acts from the center of gravity of the displaced liquid. According to Archimede’s principle the magnitude of force of buoyancy is equal to the weight of the displaced liquid.
To prove Archimede’s principle consider a body totally immersed in a liquid as shown in the figure.
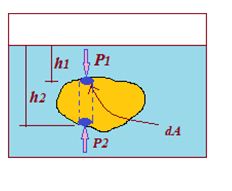
The vertical force on the body due to liquid pressure may be found most easily by considering two small elemental area dA each lying in the same vertical line shown by blue small circular areas.
The net vertical force on the body due to these elements is
dF= (P2 – P2) dA
to get the total net vertical force or upthrust on the whole body we integrate
upthrust = \left[ {\left( {{{P}_{0}}+\,\rho \int{{g{{h}_{2}}}}} \right)-\left( {{{P}_{0}}+\rho \int{{g{{h}_{1}}}}} \right)} \right]Da
upthrust = \rho \,g\int{{\left( {{{h}_{2}}-{{h}_{1}}} \right)}}\text{ }dA
But (h2 – h1) dA= dV, the volume of the part of body formed by the dotted lines as shown in the figure. Thus
Net vertical force on the body F = \rho g\int{{dV}}= V \displaystyle \rho g
here V is the submerged volume of body, in the case considered it is the whole volume of the body. It is also called the volume of displaced liquid. Since [katex] \displaystyle \rho [/katex] is he density of liquid therefore Vx[katex] \displaystyle \rho [/katex]
is the mass of displaced liquid
Force of Buoyancy or upthrust = V \displaystyle \rho g = weight of the displaced liquid
Important Points to Note
(1)
Upthrust is independent of all factors of the body such as its mass, size, density etc. except the volume of the body inside the fluid.
(2)
Upthrust depends upon the nature of displaced fluid. This is why upthrust on a fully submerged body is more in sea water than in fresh water because densityof sea water is more than that of fresh water.
(3)
Apparent weight of the body of density ( \rho ) when immersed in a liquid of density (\sigma ).
Apparent weight = Actual weight – Upthrust =W-{{F}_{{up}}} =V\rho g-V\sigma g=V(\rho -\sigma )g =V\rho g\left( {1-\frac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right)
{{W}_{{APP}}}=W\left( {1-\frac{\sigma }{\rho }} \right)
(4)
If a body of volume V is immersed in a liquid of density \sigma then its weight reduces.
{{W}_{1}}= Weight of the body in air, {{W}_{2}}= Weight of the body in water
Then apparent (loss of weight) weight {{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}}=V\sigma g
V=\frac{{{{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}}}}{{\sigma g}}
(5)
Relative density of a body
(R.D.)= \frac{{\text{density of body}}}{{\text{density of water}}}
=\frac{{\text{Weight of body}}}{{\text{Weight of equal volume of water}}}
= \frac{{\text{Weight of body}}}{{\text{Water thrust }}}
=\frac{{\text{Weight of body}}}{{\text{Loss of weight in water}}}
= \frac{{\text{Weight of body in air}}}{{\text{Weight in air–weight in water}}} = \frac{{{{W}_{1}}}}{{{{W}_{1}}-{{W}_{2}}}}
(6)
If the loss of weight of a body in water is ‘a ‘ while in liquid is ‘b‘
\frac{{{{\sigma }_{L}}}}{{{{\sigma }_{W}}}}=\frac{{\text{Upthrust on body in liquid}}}{{\text{Upthrust on body in water}}}
\displaystyle =\frac{{\text{Loss of weight in liquid}}}{{\text{Loss of weight in water}}} =\frac{a}{b}=\frac{{{{W}_{{\text{air}}}}-{{W}_{{\text{liquid}}}}}}{{{{W}_{{\text{air}}}}-{{W}_{{\text{water}}}}}}
Expression For The Immersed Volume Of Floating Body
Let a solid of volume V and density p floats in a liquid of density σ with a volume V1 immersed inside the liquid.
The weight of the floating body = V \displaystyle \rho g
The weight of the displaced liquid = V1σg
For the equilibrium of the floating body
V1σg= V \displaystyle \rho g or \frac{{{{V}_{1}}}}{V}\,\,\,\,=\,\,\,\,\frac{\rho }{\sigma } or {{V}_{1}}\,\,\,=\,\,\,\frac{\rho }{\sigma }\,\,\times \,\,V
Immersed volume = \frac{{\text{density of solid}}}{{\text{density of liquid}}}´ volume of solid = \frac{{\text{mass of solid}}}{{\text{density of liquid}}}
From the above relations it is clear that the density of the solid must be less than the density of the liquid to enable it to float freely in the liquid. However a metal vessel may float in water though the density of metal is much higher than that of water. The reason in that the floating bodies are hollow inside and hence they have a large displaced volume. When they float in water the weight of the displaced water is equal to the weight of the body.
Laws of floatation
The principle of Archimedes may be applied to floating bodies to give the laws of floatation as follows:
(i)
When a body floats freely in a liquid the weight of the body is equal to the weight of the liquid displaced.
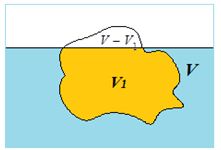
(ii)
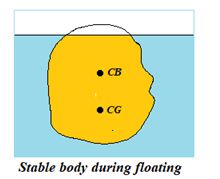
The centre of gravity of the displaced liquid (called the centre of buoyancy) lies vertically above or below the centre of gravity of the body. If it lies above the center of gravity the body is said to be in stable equilibrium during floating otherwise the body remains unstable.
Illustration
What fraction of the total volume of an iceberg floating on sea-water is exposed? The density of ice is 920 kg/m3 and that of sea-water is 1030 kg/m3.
Solution:
If V and V1 be the total and submerged volumes of the iceberg
\frac{{{{V}_{1}}}}{V}\,\,=\,\,\frac{{\text{density of iceberg}}}{{\text{density of sea-water}}}\,\,=\,\,\frac{{920}}{{1030}}\,\, =\,\,\frac{{92}}{{103}}
Now the fraction of volume exposed = \frac{{V\,\,-\,\,{{V}_{1}}}}{V}\,\,=\,\,1\,\,\,-\,\,\,\frac{{{{V}_{1}}}}{V} \,\,=\,\,1\,\,\,-\,\,\,\,\frac{{92}}{{103}}\,\,=\,\,\frac{{11}}{{103}} = 10.7%
Illustration
When a boulder of mass 240 kg is placed on a floating iceberg it is found that the iceberg just sinks. What is the mass of the iceberg? Take the relative density of ice as 0.9 and that of sea-water as 1.02.
Solution:
Let M be the weight of iceberg in kg. Then its volume
V\,\,=\,\,\frac{M}{{0.9\,\,\times \,\,{{{10}}^{3}}}}\,\,{{m}^{3}}\,\,=\,\,\frac{M}{{900}}\,\,{{m}^{3}}
When this volume just sinks under sea-water, the weight of water displaced = V´ 1020 kg.
From the principle of buoyancy, this weight must be equal to the weight of iceberg and the boulder on it.
M + 240 = \frac{M}{{900}}´ 1020 = M´ \frac{{102}}{{90}}
or M\ \left( {\frac{{102}}{{90}}\,\,-\,\,1} \right)\,\, = 240
or M\,\,=\,\,\frac{{240\,\,\times \,\,90}}{{12}}= 1800 kg
The mass of the iceberg = 1800 kg
Relative Density
In case of a liquid, sometimes another term relative density (R.D.) is defined. It is the ratio of density of the substance to the density of water at 4°C.
Hence, \text{R}\text{.D}\text{.}=\frac{{\text{Density of substance}}}{{\text{Density of water at 4}{}^\circ \text{C}}}
R.D. is a pure ratio. So, it has no units. It is also sometimes referred as specific gravity.
Density of water at 4°C in CGS is 1gm/cm3. Therefore, numerically the R.D. and density of substance (in CGS) are equal. In SI unit the density of water at 4°C is 1000 kg/m3.
Illustration
Relative density of an oil is 0.8. Find the absolute density of oil in CGS and SI units.
Solution:
Density of oil (in CGS) = (R.D.) gm/cm3
= 0.8 g/cm3
= 800 kg/m3
Density of a mixture of two or more liquids
Here, we have two cases.
Case 1: Suppose two liquids of densities \displaystyle \rho 1and \displaystyle \rho 2 having masses m1 and m2 are mixed together. Then the density of the mixture will be
\rho =\frac{{\text{Total mass}}}{{\text{Total volume}}}=\frac{{({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}{{({{V}_{1}}+{{V}_{2}})}} =\frac{{({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}})}}{{\left( {\frac{{{{m}_{1}}}}{{{{\rho }_{1}}}}+\frac{{{{m}_{2}}}}{{{{\rho }_{2}}}}} \right)}}
If m1 = m2, then \rho =\frac{{2{{\rho }_{1}}{{\rho }_{2}}}}{{{{\rho }_{1}}+{{\rho }_{2}}}}
Case 2: If two liquids of densities \displaystyle \rho 1 and \displaystyle \rho 2 having volumes V1 and V2 are mixed, then the density of the mixture is, \rho =\frac{{\text{Total mass}}}{{\text{Total volume}}}=\frac{{{{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}}}{{{{V}_{1}}+{{V}_{2}}}}=\frac{{{{\rho }_{1}}{{V}_{1}}+{{\rho }_{2}}{{V}_{2}}}}{{{{V}_{1}}+{{V}_{2}}}}
If, V1 = V2, then \rho =\frac{{{{\rho }_{1}}+{{\rho }_{2}}}}{2}.
Effect of temperature on density
As the temperature of a liquid is increased, the mass remains the same while the volume is increased and hence, the density of the liquid decreases. \left( {\text{as}\ \rho \propto \frac{1}{V}} \right).Thus,
\frac{{\rho \prime }}{\rho }=\frac{V}{{V\prime }}=\frac{V}{{V+dV}}=\frac{V}{{V+V\gamma \Delta \theta }}
or \frac{{\rho \prime }}{\rho }=\frac{1}{{1+\gamma \Delta \theta }}
Hence, g = thermal coefficient of volume expansion
and D \displaystyle \theta = rise in temperature
\rho \prime =\frac{\rho }{{1+\gamma \Delta \theta }}.
Effect of pressure on Density
As pressure is increased, volume decreases and hence density will increase. Thus, \rho \propto \frac{1}{V}
\frac{{\rho \prime }}{\rho }=\frac{V}{{V\prime }}=\frac{V}{{V+dV}}=\frac{V}{{V-\left( {\frac{{dp}}{B}} \right)V}} or \frac{{\rho \prime }}{\rho }=\frac{1}{{1-\frac{{dp}}{B}}}
Here, dp = change in pressure and B = Bulk modulus of elasticity of the liquid
Therefore, \rho \prime =\frac{\rho }{{1-\frac{{dp}}{B}}}.
Illustration
The volume of a body is V and its density is d’. Density of water is d and d’>d. The body is submerged inside water and is lifted through a height h in water. Which of the following is correct?
(a) The potential energy of the body increases by hVdg
(b) P.E. increases by hV(d’–d)g
(c) P.E. increases by hV(d’ + d)g
(d) P.E. decreases
Solution:
The resultant downward force on the sinking particle = Vd‘g – Vdg = V(d’ – d)g. When it is lifted up work is done against this force, W = hV(d’ – d)g = P.E. gained
∴ (b)
Illustration
A cubical block of wood of edge 3 cm floats in water. The lower surface of the cube just touches the free end of a vertical spring fixed at the bottom of the pot. Find the maximum weight that can be put on the block without wetting it. Density of wood = 800 kg/m3 and spring constant of the spring = 50 N/m. Take g = 10 m/s2
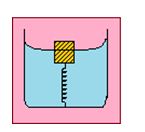
Solution:
The specific gravity of the block = 0.8. Hence the height inside water = 3 cm × 0.8 = 2.4 cm. The height outside water = 3 cm – 2.4 = i0.6 cm. Suppose the maximum weight that can be put without wetting it is W. The block in this case is completely immersed in the water. The volume of the displaced water
= volume of the block = 27 × 10–6 m3.
Hence, the force of buoyancy
= (27 × 10–6 m3) × (1000 kg/m3) × (10 m/s2)
= 0.27 N
The spring is compressed by 0.6 cm and hence the upward force exerted by the spring
= 50 N/m × 0.6 cm = 00.3 N.
The force of buoyancy and the spring force taken together balance the weight of the block plus the weight W put on the block. The weight of the block is
W’ = (27 × 10–6m) ×I (800 kg/m3) × (10 m/s2)
= 0.22 N
Thus, W = 0.27 N + 0.3 N – 0.22 N
= 0.335 N
Illustration
A metal cube floats on mercury with 1/8 th of its volume under mercury. What portion of the cube will remain under mercury if sufficient water is added just to cover the cube? Assume that the top surface of the cube remains horizontal in both cases. Relative density of mercury = 13.6.
Solution:
Let V be the volume and d the density of the cube.
Weight of the floating cube
= Vdg
= Weight of the displaced liquid
= V/8 (13.6 ´d1)g
where d1 is the density of water.
Now Vdg = V/8 x 13.6 x d1xg
d = 1.7d1 … (i)
In the second case let a volume V1 be in mercury and a volume (V – V1) in water.
Again by the principle of floatation
Vdg = V1 (13.6 d1)g + (V – V1)d1g … (ii)
From (i) and (ii)
Vx 1.7d1g = 13.6 V1× d1g + (V – V1)d1g
or 1.7V = 13.6 V1 + (V – V1)
0.7 V = 12.6 V1
or \frac{{{{V}_{1}}}}{V}\,\,=\,\,\ \frac{{0.7}}{{12.6}}\,\,\ =\,\,\ \frac{1}{{18}}
In the second case only 1/18th of the volume of the cube is under mercury.
Illustration
A wooden stick of length L, radius R and density \displaystyle \rho has a small metal piece of mass m (of negligible volume) attached to its one end. Find the minimum value for the mass m (in terms of given parameters) that would make the stick float vertically in equilibrium in a liquid of density σ.
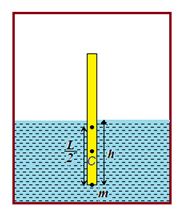
Solution:
For the stick to be vertical for rotational equilibrium, centre of gravity should be below in a vertical line through the centre of buoyancy. For minimum m, the two will coincide.
Let h be the length of immersed portion. For translator equilibrium,
Wt. of rod + mass attached = force of buoyancy
\left( {M+m} \right)g=\pi {{R}^{2}}h\sigma g … (i)
where M=\pi {{R}^{2}}L\rho .
The height of centre of mass from bottom
=\frac{{\left( M \right)L/2+m\times 0}}{{m+M}}=\frac{{ML}}{{2\left( {m+M} \right)}}
For rotatory equilibrium and for minimum m, this should be equal to h/2.
\frac{h}{2}=\frac{{ML}}{{2\left( {m+M} \right)}} … (ii)
h=\frac{{ML}}{{\left( {m+M} \right)}}
Substituting for h in equation (i), we get
\left( {M+m} \right)g=\pi {{R}^{2}}\sigma g.\frac{{ML}}{{\left( {m+M} \right)}}
{{\left( {M+m} \right)}^{2}}=\pi {{R}^{2}}\sigma .ML
\left( {M+m} \right)=\sqrt{{M\pi {{R}^{2}}\sigma L}}=\sqrt{{\pi {{R}^{2}}L\rho .\pi {{R}^{2}}\sigma L}}
m=\pi {{R}^{2}}L\sqrt{{\sigma \rho }}-\pi {{R}^{2}}L\rho =\pi {{R}^{2}}L\rho \left[ {\sqrt{{\frac{\sigma }{\rho }}}-1} \right]
Practice Questions (Basic Level)
Q.1
Equal masses of water and a liquid of specific density 2 are mixed together; then mixture has a specific density of:
(a) 2/3 (b) 4/3 (c) 3/2 (d) 3
Ans. (b)
Q.2
A beaker containing water weighs 100 g. It is placed on the pan of a balance and a piece of metal weighing 70 g and having a volume of 10 cm3 is placed inside the water in the beaker. The weight of the beaker and the metal would be:
(a) 170 g (b) 160 g (c) 100 g (d) 30 g
Ans. (a)
Q.3
When a ship floats on water:
(a) It displaces no water
(b) The mass of water displaced is equal to the mass of the ship
(c) The mass of water displaced is lesser than the mass of the ship
(d) The mass of water displaced is greater than the mass of the ship
Ans. (b)
Q.4
A solid is completelyimmersed in a liquid. The force exerted by the liquid on the solid will
(a) increase if it is pushed deeper inside the liquid
(b) change if its orientation is changed keeping it inside
(c) decrease if it is taken partially out of the liquid
(d) be in the horizontal direction only.
Ans. (c)
Q.5
When a piece of ice floating in a beaker of water completely melts, the level of water in the beaker:
(a) Rises
(b) Falls
(c) Remains unchanged
(d) Rises or falls depending upon the quantity of ice and water
Ans. (c)
Q.6
When a cube of wood floats in water, 60% of its volume is submerged. When the same cube floats in an unknown fluid, 85% of its volume is submerged. Find the densities of the wood and the unknown fluid.
(a) rwood = 4 ´ 102 kg/m3, rliquid = 7.37 ´ 102 kg/m3
(b) rwood = 6 ´ 102 kg/m3, rliquid = 6.83 ´ 102 kg/m3
(c) rwood = 6 ´ 102 kg/m3, rliquid = 7.05 ´ 102 kg/m3
(d) rwood = 7.05 ´ 102 kg/m3, rliquid = 6 ´ 102 kg/m3
Ans (c)
comprehension (Q.7 to Q.8)
A block of wood weighs 12 kg and has a relative density 0.6. It is to be in water with 0.9 of its
volume immersed. What weight of a metal is needed[R.D. of metal = 14]
Q.7
if the metal is on the top of wood
(a) 1 kg
(b) 2 kg
(c) 5 kg
(d) 6 kg
Ans (d)
Q.8
if the metal is attached below the wood?
(a) 6.5 kg
(b) 8 kg
(c) 10 kg
(d) 15 kg
Ans (a)
Q.9
A cylindrical solid body of cross-section area 50 cm2 and length 10 cm is floating on mercury with 2.5 cm of its length below the surface. Cross-section area of mercury container is 150 cm2. What is the minimum volume of water required to completely submerge the cylinder in water.
(Specific gravity of water and mercury are 1 and 13.6 respectively).
(a) 800 cm3
(b) 810 cm3
(c) 850 cm3
(d) 900 cm3
Ans(b)
Q.10
A body floats in a liquid contained in a beaker. The whole system as shown in figure falls freely under gravity. The upthrust on the body due to the liquid is:
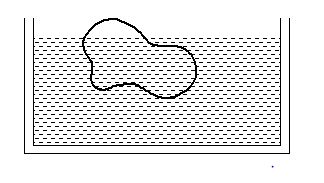
(a) Zero
(b) Equal to the weight of the liquid displaced
(c) Equal to the weight of the body in air
(d) Equal to the weight of the immersed portion of the body
Ans. (a)
Practice Questions (JEE Main Level)
Q.1
The weight of an empty balloon on a spring balance is W1. The weight becomes W2 when the balloon is filled with air. Let the weight of the air itself be W. Neglect the thickness of the balloon when it is filled with air. Also neglect the difference in the densities of air inside and outside the balloon
(a) W2 = W1 (b) W2 = W1 + W (c) W2 > W1 + W (d) W2 > W1
Ans. (a)
Q.2
A boat with scrap iron is floating in a lake. If the scrap iron is thrown in the lake the water level will:
(a) Go up (b) Go down (c) Remain unchanged (d) None of these
Ans. (b)
Q.3
An iceberg is floating partially immersed in sea water. If the density of sea water is
1.03 g cm-3 and that of ice is 0.92 g cm-3, the fraction of the total volume of iceberg above the level of sea water is:
(a) 8% (b) 11% (c) 34% (d) 89%
Ans. (b)
Q.4
A vessel contains oil (density 0.8 g cm-3) over mercury (density 13.6 g cm-3). A homogeneous sphere floats with half its volume immersed in mercury and the other half in oil. The density of the material of the sphere in g cm-3 is:
(a) 3.3 (b) 6.4 (c) 7.2 (d) 12.8
Ans. (c)
Comprehension (Q.5 to Q.6 )
A cone made of a material of relative density \left( {s=\frac{{27}}{{64}}} \right) and height 4 m floats with its apex downward in a big vessel containing water.
Q.5
Find the submerged height of cone in water
(a) h = 3 m
(b) h = 5 m
(c) h = 10 m
(d) h = 15 m
Ans (a)
Q.6
Find the time period of vertical oscillation if it is slightly disturbed from the equilibrium position.
(a) T = 0.98 s
(b) T = 1.46 s
(c) T = 0.56 s
(d) T = 1.98 s
Ans (d)
Comprehension (Q.7 to Q.8 )
A rod of length 6 m has a mass 12 kg. It is hinged at one end at a distance of 3 m below water surface.
Q.7
What weight must be attached to the other end of the rod so that 5 m of the rod is submerged?
(a) 1.26 kg
(b) 2.33 kg
(c) 5.76 kg
(d) 8.28 kg
Ans (b)
Q.8
Find the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the hinge on the rod. [Specific gravity of rod is 0.5].
(a) 50.3 N downwards
(b) 52.8 N downwards
(c) 56.7 N downwards
(d) 60.9 N downwards
Ans (c)
Q.9
A glass tube of radius 0.8 cm floats vertical in water, as shown in the figure. What mass of lead pellets would cause the tube to sink a further 3 cm?
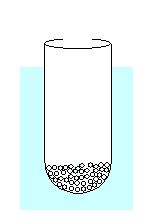
(a) 0.07 g
(b) 2.664 g
(c) 9.234 g
(d) 9.03 g
Ans (d)
Q.10
The tension in a string holding a solid block below the surface of a liquid (of density greater than that of solid) as shown in the figure is To when the system is at rest. What will be the tension in the string if the system has upward acceleration a?
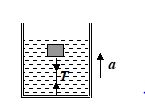
(a) T = To[1 + (a/2g)]
(b) T = To[1 + (2a/g)]
(c) T = To[3 + (a/g)]
(d) T = To[1 + (a/g)]
Ans (d)
Practice Questions (JEE Advance Level)
Q.1
A large block of ice 5 m thick has a vertical hole drilled through it floating in the middle of a lake. What is the minimum length of a rope required to scoop up a bucket-full of water through the hole?
[R.D. of ice = 0.9]
(a) 0.1 m
(b) 0.5 m
(c) 2.6 m
(d) 5.3 m
Ans (b)
Q.2
A cylindrical buoy 2 m in length and 0.75 m in diameter is constructed of a material with a specific gravity of 0.6. One end of a light cord is attached to the bottom of the buoy, and the other is fixed to an anchor that rests at the bottom of the waterway. If only 0.4 m of the buoy remains above water, what is the tension in the cord?
(a) 0.46 ´ 103 N
(b) 1.73 ´ 103 N
(c) 5.38 ´ 103 N
(d) 9.46 ´ 103 N
Ans (b)
Q.3
A body of density r is dropped from rest from a height h into a lake of density s (s > r). The maximum depth the body sinks inside the liquid is (neglect viscous effect of liquid)
(a) \frac{{h\rho }}{{\sigma -\rho }}
(b) \frac{{h\rho }}{{\sigma +\rho }}
(c) \frac{{h\rho }}{\sigma }
(d) \frac{{h\sigma }}{\rho }
Ans. (a)
Comprehension (Q.7 to Q.8 )
A container of large uniform cross-sectional area A resting on a horizontal surface, holds two immiscible, non-viscous and incompressible liquids of densities d and 2d, each of height H/2 as shown in figure. The lower density of liquid is open to the atmosphere having pressure Po. A homogeneous solid cylinder of length L (L>H/2), cross-sectional area A/5 is immersed such that it floats with its axis vertical at the liquid-liquid interface with length L/4 in the denser liquid. Determine
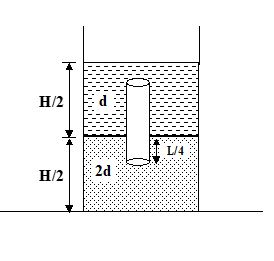
Q.4
the density D of the solid, and
(a) \frac{{4d}}{5}
(b) \frac{{5d}}{4}
(c) \frac{{3d}}{4}
(d) \frac{{4d}}{3}
Ans (b)
Q.5
the total pressure at the bottom of the container
(a) \frac{{\left( {6H-L} \right)}}{4}dg+{{P}_{o}}
(b) \frac{{\left( {6H+2L} \right)}}{5}dg+{{P}_{o}}
(c) \frac{{\left( {6H+L} \right)}}{4}dg+{{P}_{o}}
(d) \frac{{\left( {6H+3L} \right)}}{3}dg+{{P}_{o}}
Ans (c)
Q.6
A solid cone of height H, radius R suspended by a string is just submerged in a liquid of density r as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the net force applied by the liquid on the curved surface of the cone is equal to (atmospheric pressure is Po)
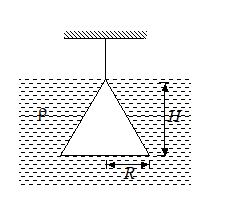
(a) \frac{{\pi {{R}^{2}}}}{3}\left( {2{{P}_{o}}+\rho gH} \right)
(b) \frac{{\pi {{R}^{3}}}}{3}\left( {2{{P}_{o}}-\rho gH} \right)
(c) \frac{{\pi {{R}^{2}}}}{3}\left( {3{{P}_{o}}+2\rho gH} \right)
(d) \frac{{\pi {{R}^{2}}}}{3}\left( {3{{P}_{o}}-2\rho gH} \right)
Ans. (c)
Q.7
A block of mass 10 kg connected to another hollow block of same size and negligible mass, by a spring of spring constant 500 N/m, floats in water as shown in the figure. The compression in the spring is (rwater = 1 ´ 103 kg/m3, g = 10 m/s2)
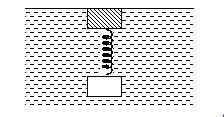
(a) 10 cm (b) 20 cm (c) 50 cm (d) 100 cm
Ans. (a)
Comprehension (Q.8 to Q.10 )
A uniform solid cylinder of density 0.8 g/cm3 floats in equilibrium in a combination of two non-mixing liquids A and B with its axis vertical. The densities of the liquids A and B are 0.7 g/cm3 and 1.2 g/cm3, respectively. The height of liquid A is hA= 1.2 cm. The length of the part of the cylinder immersed in liquid B is hB= 0.8 cm.
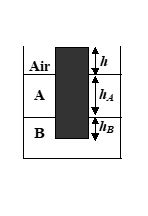
Q.8
Find the total force exerted by liquid A on the cylinder.
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 10
(d) 20
Ans (a)
Q.9
Find h, the length of the part of the cylinder in air.
(a) 1.38 cm
(b) 0.25 cm
(c) 6.56 cm
(d) 10.53 cm
Ans (b)
Q.10
The cylinder is depressed in such a way that its top surface is just below the upper surface of liquid A and is then released. Find the acceleration of the cylinder immediately after it is released.
(a) 2g/6 (upward)
(b) g/6 (upward)
(c) 5g/6 (upward)
(d) g/4 (upward)
Ans (b)
Q.11
In the given figure, a container contains liquid whose density varies with height h from the bottom as
r= {{\rho }_{o}}\left( {4-\frac{{3h}}{{{{h}_{o}}}}} \right). Here is a constant, and ho is the height of the liquid in the container. A small solid block of density \frac{5}{2}{{\rho }_{o}} and mass m is released from the bottom of the tank. Show that the block will execute SHM. Also find the frequency of oscillation.
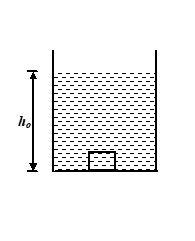
(a) f=\frac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{6g}}{{5{{h}_{o}}}}}}
(b) f=\frac{1}{{5\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{6g}}{{5{{h}_{o}}}}}}
(c) f=\frac{1}{{2\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{g}}{{5{{h}_{o}}}}}}
(d) f=\frac{1}{{5\pi }}\sqrt{{\frac{{6g}}{{5{{h}_{o}}}}}}
Ans (a)
