1.
What will be the equivalent resistance between the two points A and D ?
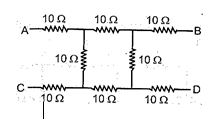
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 30
(d) 40
Ans. (c)
Q.2
What is the potential difference across the points A and B ?
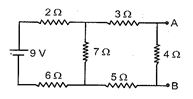
(a) 0.9 V
(b) 1.1 V
(c) 1.3 V
(d) 0.7 V
Ans. (b)
Q.3
A parallel combination of three resistors takes a current of 7.5 A from a 30 V supply. If the two resistors are 10 \displaystyle \Omega and 12 \displaystyle \Omega , find which is the third one ?
(a) 4 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 15 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) 12 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 22 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans. (b)
Q.4
In the given figure the equivalent resistance between A and B is :
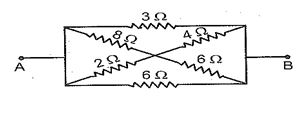
(a) 17/24 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 4/3 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) 29 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 24/17 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans. (b)
Q.5
In the figure shown, potential drop across the 3 \displaystyle \Omega resistor is :
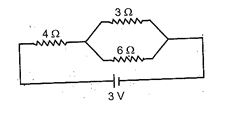
(a) 1 V
(b) 1.5V
(c) 2 V
(d) 2.5 V
Ans. (a)
Q.6
The current flowing in the electrical circuit is 1A. If we replace all the 4 \displaystyle \Omega resistances with a 2 \displaystyle \Omega resistance, then the value of the current in the circuit will be :
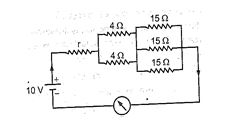
(a) 1.11 A
(b) 2.11 A
(c) 3.11 A
(d) 4.11 A
Ans. (a)
Q.7
The potential difference across 8 ohm resistance is 48 V shown in figure. The value of potential difference across X and Y point will be :
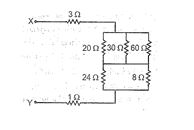
(a) 160 V
(b) 128 V
(c) 80 V
(d) 62 V
Ans. (a)
Q.8
A battery of e.m.f. 10 V is connected to resistances as shown in figure. The potential difference between A and B \displaystyle \left( {{{V}_{A}}-{{V}_{B}}} \right) is :
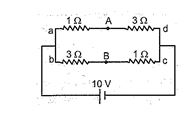
(a) –2V
(b) 2 V
(c) 5 V
(d) (20/11) V
Ans. (c)
Q.9
Calculate net resistance between A and B :
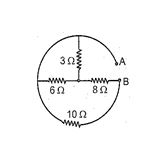
(a) 3 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 5 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) 6 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 8 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans. (b)
Q. 10
Calculate net resistance between A and B :
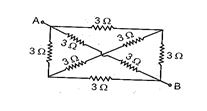
(a) 2 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 3 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) 4 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 5 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans. (a)
Q.11
Find the equivalent resistance between the terminals A and B.
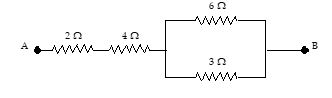
(a) 4 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 8 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) 12 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 22 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans : (b)
Q.12
Find the equivalent resistance between point a and b for the combination shown in figure.
(a) 4 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 15 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) 12 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 9 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans. (c)
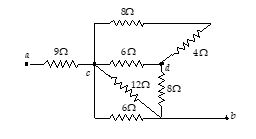
Q.13
The three resistors in figure are R1 = 80 \displaystyle \Omega , R2 = 25 \displaystyle \Omega , R3 = 15 \displaystyle \Omega . What are the current I and I2, and the voltage across the battery, if I1 = 0.3 A?
(a) 0.9A, 0.6A
(b) 1.9A, 1.6A
(c) 2.9A, 2.6A
(d) 0.3A, 0.1A
Ans. (a)
Q.14
For the circuit shown, find the current through the branch ab.
(a) 0.4 A
(b) 1.5A
(c) 0.5A
(d) 1.9A
Ans. (c)
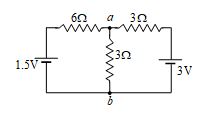
Q.15
In the given circuit resistance of voltmeter is 400\Omega and its reading is 20V. Find the value of emf of battery
(a) 130/3 volt
(b) 65 volt
(c) 40 volt
(d) 33.6 volt
Ans : (a)
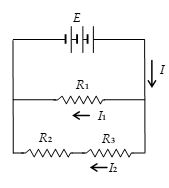
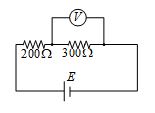
16.
The total current supplied to the circuit by the battery is
(a) 1A
(b) 2A
(c) 4A
(d) 6A
Ans. (c)
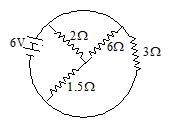
Q.17
The reading of the ammeter in the figure shown is
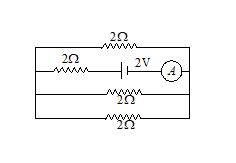
(a) \frac{1}{8}A
(b) \frac{3}{4}A
(c) \frac{1}{2}A
(d) 2A
Ans. (b)
Q.18
In the circuit shown, current through 3 \displaystyle \Omega resistance is
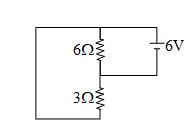
(a) 1 amp
(b) 2 amp
(c) 3 amp
(d) 4 amp
Ans. (b)
Q.19
The electric potential variation around a single closed loop containing an ideal battery and one or more resistors as shown in figure. If current of flows in the circuit, the circuit can not have
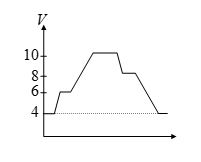
(a) two resistors and two batteries
(b) one resistor and three batteries
(c) maximum net emf of 6 volt
(d) three resistor and one battery
Ans : (d)
Q.20
The possible circuit of close loop corresponding to the graph of previous question is
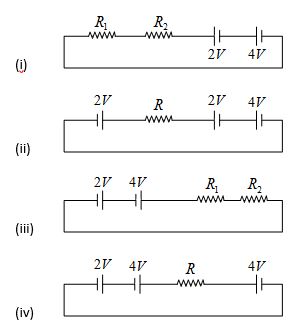
Ans. (iv)
Q.21
In the diagram shown, the reading of voltmeter is 20 V and that of ammeter is 4A. The value of R should be (Consider given ammeter and voltmeter are not ideal)
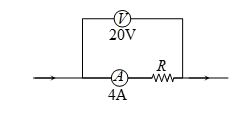
(a) Equal to 5 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) Greater from 5 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) Less than 5 \displaystyle \Omega
(d) Greater or less than 5 \displaystyle \Omega depends on the material of R
Ans. (c)
Q.22
In the circuit shown in figure, equivalent resistance between A and B is
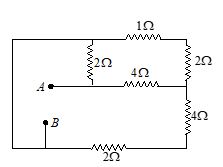
(a) 8 \displaystyle \Omega
(b) 15 \displaystyle \Omega
(c) \frac{3}{2} \displaystyle \Omega
(d) 2 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans. (c)
