Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
1.
Magnetic moments of two bar magnets may be compared with the help of
(a) Deflection magnetometer
(b) Vibration magnetometer
(c) Both of the above
(d) None of the above
Ans (c)
2.
The time period of oscillation of a freely suspended bar magnet with usual notations is given by
(a) T=2\pi \sqrt{{\frac{I}{{M{{B}_{H}}}}}}
(b) T=2\pi \sqrt{{\frac{{M{{B}_{H}}}}{I}}}
(c) T=\sqrt{{\frac{I}{{M{{B}_{H}}}}}}
(d) T=2\pi \sqrt{{\frac{{{{B}_{H}}}}{{MI}}}}
Ans (a)
3.
In sum and difference method in vibration magnetometer, the time period is more if
(a) Similar poles of both magnets are on same sides
(b) Opposite poles of both magnets are on same sides
(c) Both magnets are perpendicular to each other
(d) Nothing can be said
Ans (b)
4.
Vibration magnetometer before use, should be set
(a) In magnetic meridian
(b) In geographical meridian
(c) Perpendicular to magnetic meridian
(d) In any position
Ans (a)
5.
Magnets A and B are geometrically similar but the magnetic moment of A is twice that of B. If T1 and T2 be the time periods of the oscillation when their like poles and unlike poles are kept together respectively, then \frac{{{{T}_{1}}}}{{{{T}_{2}}}}will be
(a) \frac{1}{3}
(b) \frac{1}{2}
(c) \frac{1}{{\sqrt{3}}}
(d) \sqrt{3}
Ans (c)
6.
Vibration magnetometer works on the principle of
(a) Torque acting on the bar magnet
(b) Force acting on the bar magnet
(c) Both the force and the torque acting on the bar magnet
(d) None of these
Ans (a)
7.
Tangent galvanometer is used to measure
(a) Steady currents
(b) Current impulses
(c) Magnetic moments of bar magnets
(d) Earth’s magnetic field
Ans (a)
8.
The sensitivity of a tangent galvanometer is increased if
(a) Number of turn decreases
(b) Number of turn increases
(c) Field increases
(d) None of the above
Ans (b)
9.
The period of oscillations of a magnetic needle in a magnetic field is 1.0 sec. If the length of the needle is halved by cutting it, the time period will be
(a) 1.0 sec
(b) 0.5 sec
(c) 0.25 sec
(d) 2.0 sec
Ans (b)
10.
The time period of oscillation of a bar magnet suspended horizontally along the magnetic meridian is T0. If this magnet is replaced by another magnet of the same size and pole strength but with double the mass, the new time period will be
(a) \frac{{{{T}_{0}}}}{2}
(b) \frac{{{{T}_{0}}}}{{\sqrt{2}}}
(c) \sqrt{2}{{T}_{0}}
(d) 2{{T}_{0}}
Ans (c)
11.
Which of the following statement is not the true
(a) While taking reading of tangent galvanometer, the plane of the coil must be set at right angles to the earth’s magnetic meridian
(b) A short magnet is used in a tangent galvanometer since a long magnet would be heavy and may not easily move
(c) Measurements with the tangent galvanometer will be more accurate when the deflection is around 45o
(d) A tangent galvanometer can not be used in the polar region
Ans (a)
12.
A magnet oscillating in a horizontal plane has a time period of 2 second at a place where the angle of dip is 30o and 3 seconds at another place where the angle of dip is 60o. The ratio of resultant magnetic fields at the two places is
(a) \frac{{4\sqrt{3}}}{7}
(b) \frac{4}{{9\sqrt{3}}}
(c) \frac{9}{{4\sqrt{3}}}
(d) \frac{9}{{\sqrt{3}}}
Ans (c)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
1.
At a certain place a magnet makes 30 oscillations per minute. At another place where the magnetic field is double, its time period will be
(a) 4 sec
(b) 2 sec
(c) \frac{1}{2}\sec
(d) \sqrt{2}\sec
Ans (d)
2.
Time period for a magnet is T. If it is divided in four equal parts along its axis and perpendicular to its axis as shown then time period for each part will be
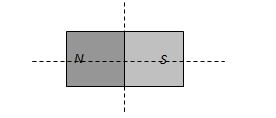
(a) 4T
(b) T/4
(c) T/2
(d) T
Ans (c)
3.
A magnet is suspended in such a way that it oscillates in the horizontal plane. It makes 20 oscillations per minute at a place where dip angle is 30o and 15 oscillations per minute at a place where dip angle is 60o. The ratio of total earth’s magnetic field at the two places is
(a) 3\sqrt{3}:8
(b) 16:9\sqrt{3}
(c) 4:9
(d) 2\sqrt{3}:9
Ans (b)
4.
Two magnets A and B are identical in mass, length and breadth but have different magnetic moments. In a vibration magnetometer, if the time period of B is twice the time period of A. The ratio of the magnetic moments {{M}_{A}}/{{M}_{B}} of the magnets will be
(a) 1/2
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 1/4
Ans (c)
5.
A magnet of magnetic moment M oscillating freely in earth’s horizontal magnetic field makes n oscillations per minute. If the magnetic moment is quadrupled and the earth’s field is doubled, the number of oscillations made per minute would be
(a) \frac{n}{{2\sqrt{2}}}
(b) \frac{n}{{\sqrt{2}}}
(c) 2\sqrt{2}n
(d) \sqrt{2}n
Ans (c)
6.
A small bar magnet A oscillates in a horizontal plane with a period T at a place where the angle of dip is 60o. When the same needle is made to oscillate in a vertical plane coinciding with the magnetic meridian, its period will be
(a) \frac{T}{{\sqrt{2}}}
(b) T
(c) \sqrt{2}T
(d) 2T
Ans (a)
7.
A tangent galvanometer has a coil with 50 turns and radius equal to 4 cm. A current of 0.1 A is passing through it. The plane of the coil is set parallel to the earth’s magnetic meridian. If the value of the earth’s horizontal component of the magnetic field is 7\times {{10}^{{-5}}}tesla and {{\mu }_{0}}=4\pi \times {{10}^{{-7}}}weber/amp\times m, then the deflection in the galvanometer needle will be
(a) 45o
(b) 48.2o
(c) 50.7o
(d) 52.7o
Ans (b)
8.
Two tangent galvanometers having coils of the same radius are connected in series. A current flowing in them produces deflections of 60° and 45° respectively. The ratio of the number of turns in the coils is
(a) 4/3
(b) (\sqrt{3}+1)/1
(c) (\sqrt{3}+1)/(\sqrt{3}-1)
(d) \sqrt{3}/1
Ans (d)
9.
Using a bar magnet P, a vibration magnetometer has time period 2seconds. When a bar Q (identical to P in mass and size) is placed on top of P, the time period is unchanged. Which of the following statements is true
(a) Q is of non-magnetic material
(b) Q is a bar magnet identical to P, and its north pole placed on top of P‘s north pole
(c) Q is of unmagnetized ferromagnetic material
(d) Nothing can be said about Q‘s properties
Ans (b)
10.
A certain amount of current when flowing in a properly set tangent galvanometer, produces a deflection of 45°. If the current be reduced by a factor of \sqrt{3}, the deflection would
(a) Decrease by 30°
(b) Decrease by 15°
(c) Increase by 15°
(d) Increase by 30°
Ans (b)
11.
The bob of a simple pendulum is replaced by a magnet. The oscillations are set along the length of the magnet. A copper coil is added so that one pole of the magnet passes in and out of the coil. The coil is short-circuited. Then which one of the following happens
(a) Period decreases
(b) Period does not change
(c) Oscillations are damped
(d) Amplitude increases
Ans (c)
12.
Two short magnets having magnetic moments in the ratio 27 : 8, when placed on opposite sides of a deflection magnetometer, produce no deflection. If the distance of the weaker magnet is 0.12 m from the centre of deflection magnetometer, the distance of the stronger magnet from the centre is
(a) 0.06 m
(b) 0.08 m
(c) 0.12 m
(d) 0.18 m
Ans (d)
13.
A thin rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely in the same field. If its period of oscillation is T ¢, then ratio \frac{{{T}’}}{T}is
(a) \frac{1}{4}
(b) \frac{1}{{2\sqrt{2}}}
(c) \frac{1}{2}
(d) 2
Ans (c)
14.
Two identical bar magnets are placed on above the other such that they are mutually perpendicular and bisect each other. The time period of this combination in a horizontal magnetic Field is T. The time period of each magnet in the same field is
(a) {{2}^{{\frac{1}{4}}}}T
(b) {{2}^{{-\frac{1}{4}}}}T
(c) {{2}^{{-\frac{1}{2}}}}T
Ans (b)
