Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
Q.1
A conducting circular loop of radius r carries a constant current I. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field \vec{B} such that \vec{B} is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The magnetic force acting on the loop is
(a) BIr (b) 2pIrB (c) zero (d) 2IrB
Ans. (c)
Q.2
A particle having mass m and charge q is attached to one end of a light rigid rod of length l. The rod is rotated at constant angular velocity about an axis normal to its length and passing through rod’s other free end. The ratio of the magnitude of the magnetic moment of the system and its angular momentum equals.
(a) \frac{q}{{2m}}
(b) \frac{1}{{m{{l}^{2}}}}
(c) \frac{q}{m}
(d) \frac{1}{{\pi m}}
Ans. (a)
Q.3
An insulating rod of length l carries a charge q distributed uniformly on it. The rod is pivoted at an end and is rotated at a frequency f about a fixed perpendicular axis. The magnetic moment of the system is
(a) zero
(b) \displaystyle \pi q f l2
(c) \frac{1}{2} \displaystyle \pi q f l2
(d) \frac{1}{3} \displaystyle \pi q f l2
Ans : (d)
4.
A circular coil of 30 turns and radius 8.0 cm carrying a current of 6.0 A is suspended vertically in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 1.0 T. The field lines make an angle of 60° with the normal to the coil. Calculate the magnitude of counter torque that must be applied to prevent the coil from turning.
(a) 3.25 Nm
(b) 3.14 Nm
(c) 3.00Nm
(d) 3.50 Nm
Ans (b)
5.
A coil in the shape of an equilateral triangle of side 0.02 m is suspended from a vertex such that it is hanging in a vertical plane between the pole pieces of a permanent magnet producing a horizontal magnetic field of 5\times {{10}^{{-2}}}T. Find the couple acting on the coil. When a current of 0.1 ampere is passed through it and the magnetic field is parallel to its plane.
(a) 7.5\times {{10}^{{-7}}}\,N-m
(b) 8.00\times {{10}^{{-7}}}\,N-m
(c) 8.66\times {{10}^{{-7}}}\,N-m
(d) 9.0\times {{10}^{{-7}}}\,N-m
Ans (c)
6.
A circular coil of 200 turns, radius 5 cm carries a current of 2.5 A. It is suspended vertically in uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.25 T, with the plane of the coil making an angle of 60° with the field lines. Calculate the magnitude of ht torque that must be applied on it to prevent if from turning.
(a) 0.60 Nm
(b) 0.49 Nm
(c) 0.25 Nm
(d) 0.30 Nm
Ans (b)
7.
The resistance of an ammeter of 1–ampere range is 1 ohm. Calculate the resistance of the shunt, which will increase the range of the ammeter to 10 amperes.
(a) \frac{1}{5}\,\,\Omega
(b) \frac{1}{9}\,\,\Omega
(c) \frac{1}{3}\,\,\Omega
(d) \frac{1}{15}\,\,\Omega
Ans (b)
8.
A voltmeter has got a resistance of . What alteration in it will have to be made so as to increase its range twenty times?
(a) 90000\,\,\Omega
(b) 85000\,\,\Omega
(c) 5000\,\,\Omega
(d) 95000\,\,\Omega
Ans (d)
9.
A cyclotron’s oscillator frequency is 1 MHz. What should be the operating magnetic field for accelerating protons? If the radius of the Dees is 60 cm, what is the kinetic energy of the proton beam? {{m}_{p}}=1.67\times {{10}^{{-27}}}\,\,kg. Express your result in MeV (1 MeV=1.6\times {{10}^{{-13}}}\,\,J)
(a)0.60T, 7.2 MeV
(b)0.50T, 6.5 MeV
(c)0.66T, 7.4 MeV
(d)0.80T, 8.0 MeV
Ans (c)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
Q.1
A rectangular loop carrying a current i is situated near a long, straight wire such that the wire is parallel to one of the sides of the loop and is in the plane of the loop. If a steady current I is established in the wire as shown in the figure the loop will
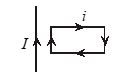
(a) rotate about an axis parallel to the wire
(b) move away from the wire
(c) move towards the wire
(d) Both (1) and (3)
Ans : (c)
Q.2
In the following figures which one correspond to the stable equilibrium position?
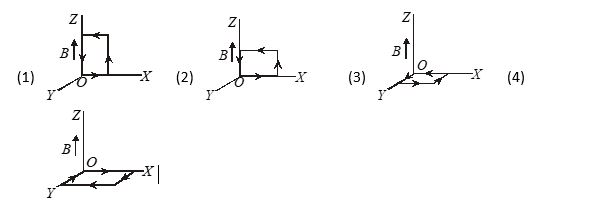
Ans : (3)
Q.3
A rectangular loop is placed in a vertical plane as shown in the figure. It has area A, and a current i is flowing through it in anticlockwise direction. Find the torque acting on it , if it is placed in a horizontal magnetic field B making an angle \theta with the loop.
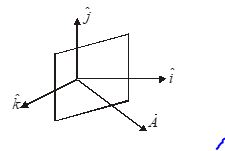
(a) B\,i\,A\,\hat{i}
(b) B\,i\,A\,\sin \theta \,\hat{k}
(c) B\,i\,A\,\cos \theta \,\hat{j}
(d) B\,i\,A\,\tan \theta \,\hat{k}
Ans : (c)
Q.4
A rectangular coil of size 3.0\,\,cm\times 4.0\,\,cm and having 100 turns is provided about the Z-axis as shown in figure. The coil carries an electric current of 2.0 A and a magnetic field of 1.0 T is present along the Y–axis. Find the torque acting on the coil if the side in the X–Y plane makes an angle \theta =37{}^\circ with the X–axis.
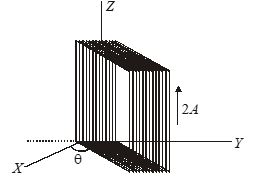
(a) 0.28 N – m
(b) 0.14 N – m
(c) 0.37 N – m
(d) 0.47 N – m
Ans. (b)
Q.5
An insulating rod of length l carries a charge q distributed uniformly on it. The rod is pivoted at an end and is rotated at a frequency f about a fixed perpendicular axis. The magnitude moment of the system is
(a) Zero
(b) \pi q\,f\,{{l}^{2}}
(c) \frac{1}{2}\pi q\,f\,{{l}^{2}}
(d) \frac{1}{3}\pi q\,f\,{{l}^{2}}
Ans. (d)
Q.6
A soft iron cylinder is used in a moving coil galvanometer, because without it
(a) The galvanometer will not work at all
(b) The magnetic field will not be uniformly radial
(c) The electric field will not be very strong
(d) The coil will not rest in position
Ans: (b)
Q.7
The magnetic field between the cylindrical pole piece used in the construction of the moving coil galvanometer is
(a) Rectangular throughout the space
(b) Rectangular only near the poles
(c) Radial through out the space
(d) Radial only near the poles
Ans : 4
Q.8
The sensitivity of a suspended type moving coil galvanometer will
(a) Increase if the length of the suspension wire is increased
(b) Decrease if the length is increased
(c) Remain unaffected by the change of the length of the suspension
(d) Increase if it is shortened
Ans (a)
Q.9
When a galvanometer coil of resistance G is shunted to send \frac{1}{n}th of the main current through it, the effective resistance of the galvanometer is
(a) nG
(b) (n-1)G
(c) \frac{G}{n}
(d) (n+1)G
Ans : (c)
Q.10
When a galvanometer of resistance g is shunted by a shunt S, the resistance of the circuit decreased by
(a) g-S
(b) \frac{{{{g}^{2}}}}{S}
(c) \frac{{{{g}^{2}}}}{{g+S}}
(d) \frac{g}{{g+S}}
Ans : (c)
Q.11
A radial field is purposely used in a moving coil galvanometer because
(a) Without it the galvanometer will not work at all.
(b) The galvanometer will work, but its deflection will not be proportional to the current
(c) The galvanometer will work and its deflection will be linearly proportional to the current
(d) The galvanometer will work, but its deflection will be proportional to \displaystyle \cos \theta , where \theta is the deflection of the coil
Ans : (c)
Q.12
To increase the range of an ammeter of resistance \gamma ohm n times, the shunt required is
(a) nr
(b) \frac{r}{n}
(c) \frac{r}{{n-1}}
(d) \frac{r}{{n+1}}
Ans : (c)
Q.13
A galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by connecting
(a) A low resistance in series with it
(b) A low resistance in parallel to it
(c) A high resistance in series with
(d) A high resistance in parallel to it
Ans : (b)
Q.14
If 10% of the main current is to be passed through a moving coil galvanometer of resistance 99\,\,\Omega , then the required shunt resistance will be
(a) 9.9\,\,\Omega
(b) 10\,\,\Omega
(c) 11\,\,\Omega
(d) 9\,\,\Omega
Ans. (c)
Q.15
Choose the wrong statement. The sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer can be increased by
(a) Increasing the number of turns in the coil
(b) Inserting a soft iron cylinder inside the coil
(c) Increasing the strength of the magnetic field
(d) Using a suspension fibre of a higher restoring couple per unit twist
Ans. (d)
