Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
1.
The magnetism of magnet is due to
(a) The spin motion of electron
(b) Earth
(c) Pressure of big magnet inside the earth
(d) Cosmic rays
Ans (a)
2.
The pole strength of a bar magnet is 48 ampere-metreand the distance between its poles is 25 cm. The moment of the couple by which it can be placed at an angle of 30o with the uniform magnetic intensity of flux density 0.15 Newton /ampere-metre will be
(a) 12 Newton × metre
(b) 18 Newton × metre
(c) 0.9 Newton × metre
(d) None of the above
Ans (c)
3.
The magnetic field at a point x on the axis of a small bar magnet is equal to the field at a point y on the equator of the same magnet. The ratio of the distances of x and y from the centre of the magnet is
(a) {{2}^{{-3}}}
(b) {{2}^{{-1/3}}}
(c) {{2}^{3}}
(d) {{2}^{{1/3}}}
Ans (d)
4.
A magnet of magnetic moment M is situated with its axis along the direction of a magnetic field of strength B. The work done in rotating it by an angle of 180o will be
(a) -MB
(b) +MB
(c) 0
(d) +2MB
Ans (d)
5.
A long magnet is cut in two parts in such a way that the ratio of their lengths is 2 : 1. The ratio of pole strengths of both the section is
(a) Equal
(b) In the ratio of 2 : 1
(c) In the ratio of 1 : 2
(d) In the ratio of 4 : 1
Ans (a)
6.
A long magnetic needle of length 2L, magnetic moment M and pole strength m units is broken into two pieces at the middle. The magnetic moment and pole strength of each piece will be
(a) \frac{M}{2},\frac{m}{2}
(b) M,\frac{m}{2}
(c) \frac{M}{2},m
(d) M,m
Ans (c)
7.
Force between two unit pole strength placed at a distance of one metre is
(a) 1 N
(b) \frac{{{{{10}}^{{-7}}}}}{{4\pi }}N
(c) {{10}^{{-7\,}}}\,N
(d) 4\pi \times {{10}^{{-7}}}N
Ans (c)
8.
Two equal bar magnets are kept as shown in the figure. The direction of resultant magnetic field, indicated by arrow head at the point P is (approximately)
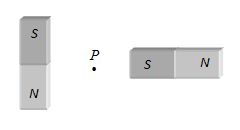
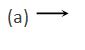
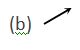
Ans (b)
9.
A short bar magnet placed with its axis at 30° with a uniform external magnetic field of 0.16 Tesla experiences a torque of magnitude 0.032 Joule. The magnetic moment of the bar magnet will be
(a) 0.23 Joule/Tesla
(b) 0.40 Joule/Tesla
(c) 0.80Joule/Tesla
(d) Zero
Ans (b)
10.
Two magnets, each of magnetic moment ‘M’ are placed so as to form a cross at right angles to each other. The magnetic moment of the system will be
(a) 2 M
(b) \sqrt{2}\,M
(c) 0.5 M
(d) M
Ans (b)
11.
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 3.0 A-m2 is placed in a uniform magnetic induction field of 2 ´ 10–5 T. If each pole of the magnet experiences a force of 6 ´ 10–4N, the length of the magnet is
(a) 0.5 m
(b) 0.3 m
(c) 0.2 m
(d) 0.1 m
Ans (d)
12.
A bar magnet of length 3 cm has points A and B along its axis at distances of 24 cm and 48 cm on the opposite sides. Ratio of magnetic fields at these points will be
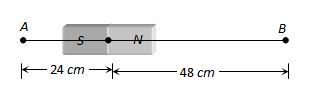
(a) 8
(b) 1/2\,\,\sqrt{2}
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans (a)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
Q.1
The magnetic needle in a tangent galvanometer is essentially small, because
(a) The earth’s field is not uniform over a sufficiently wide region
(b) The field due to the current is not uniform over a wide region
(c) A very strong field is required to deflect a long needle
(d) It is difficult to construct a long needle of uniform magnetization
Ans : (b)
Q.2
The reduction factor of a tangent galvanometer is (symbols have their own meaning)
(a) \frac{{{{B}_{0}}a}}{N}
(b) \frac{{2a{{B}_{0}}}}{{{{\mu }_{0}}N}}
(c) \frac{{a{{H}_{0}}}}{N}
(d) \frac{{2a{{H}_{0}}}}{{{{\mu }_{0}}N}}
Ans : (b)
Q.3
The deflection in a tangent galvanometer should be nearly 45°, because
(a) tan 45° being equal to 1, it becomes very easy to calculate the value of the current
(b) The percentage error in the measurement is a minimum
(c) The galvanometer is most sensitive, when the deflection is 45°
(d) 45° is just half of 90°
Ans : (b)
Q.4
The reduction factor of a tangent galvanometer for a given coil is numerically equal to the current which produces a deflection of
(a) 1° (b) 30° (c) 45° (d) 90°
Ans (c)
5.
A bar magnet having centre O has a length of 4 cm. Point P1 is in the broad side-on and P2 is in the end side-on position with OP1 = OP2 = 10 metres. The ratio of magnetic intensities H at P1 and P2 is
(a) {{H}_{1}}:{{H}_{2}}=16:100
(b) {{H}_{1}}:{{H}_{2}}=1:2
(c) {{H}_{1}}:{{H}_{2}}=2:1
(d) {{H}_{1}}:{{H}_{2}}=100:16
Ans (d)
6.
Points A and B are situated perpendicular to the axis of a 2cm long bar magnet at large distances X and 3X from its centre on opposite sides. The ratio of the magnetic fields at A and B will be approximately equal to
(a) 1 : 9
(b) 2 : 9
(c) 27 : 1
(d) 9 : 1
Ans (c)
7.
Two short magnets with their axes horizontal and perpendicular to the magnetic meridian are placed with their centres 40 cm east and 50 cm west of magnetic needle. If the needle remains undeflected, the ratio of their magnetic moments \displaystyle {{M}_{1}}:{{M}_{2}} is
(a) 4 : 5
(b) 16 : 25
(c) 64 : 125
(d) 2:\sqrt{5}
Ans (c)
8.
Rate of change of torque with deflectionis maximum for a magnet suspended freely in a uniform magnetic field of induction B, when
(a) \theta =0{}^\circ
(b) \theta =45{}^\circ
(c) \theta =60{}^\circ
(d) \theta =90{}^\circ
Ans (a)
9.
A straight wire carrying current iis turned into a circular loop. If the magnitude of magnetic moment associated with it in M.K.S. unit is M, the length of wire will be
(a) 4\pi iM
(b) \sqrt{{\frac{{4\pi M}}{i}}}
(c) \sqrt{{\frac{{4\pi i}}{M}}}
(d) \frac{{M\pi }}{{4i}}
Ans (b)
10.
Two similar bar magnets P and Q, each of magnetic moment M, are taken, If P is cut along its axial line and Q is cut along its equatorial line, all the four pieces obtained have
(a) Equal pole strength
(b) Magnetic moment \frac{M}{4}
(c) Magnetic moment \frac{M}{4}
(d) Magnetic moment M
Ans (c)
11.
A magnet of magnetic moment 50\,\hat{i}\,A\text{-}{{m}^{2}} is placed along the x-axis in a magnetic field \overrightarrow{B}=(0.5\,\hat{i}+3.0\hat{j})\,T. The torque acting on the magnet is
(a) 175 \hat{k}\,\,N\text{-}m
(b) 150 \hat{k}\,\,N\text{-}m
(c) 75 \hat{k}\,\,N\text{-}m
(d) 25\sqrt{{37}}\,\hat{k}\,\,N\text{-}m
Ans (b)
12.
The magnetic potential at a point on the axial line of a bar magnet of dipole moment M is V. What is the magnetic potential due to a bar magnet of dipole moment \frac{M}{4} at the same point
(a) 4\,V
(b) 2\,V
(c) \frac{V}{2}
(d) \frac{V}{4}
Ans (d)
13.
Two identical short bar magnets, each having magnetic moment of 10 Am2, are arranged such that their axial lines are perpendicular to each other and their centres be along the same straight line in a horizontal plane. If the distance between their centres is 0.2 m, the resultant magnetic induction at a point midway between them is ({{\mu }_{0}}=4\pi \times {{10}^{{-7}}}H{{m}^{{-1}}})
(a) xy Tesla
(b) \sqrt{5}\times {{10}^{{-7}}}Tesla
(c) \sqrt{2}\times {{10}^{{-3}}}Tesla
(d) \sqrt{5}\times {{10}^{{-3}}}Tesla
Ans (d)
