Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
Q. 1
An electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field experiences, in general
(a) a force and a torque
(b) a force only
(c) a torque only
(d) neither a force nor a torque
Ans. (c)
Q.2
A and B are two points on the axis and the perpendicular bisector respectively of an electric dipole. And B are far away from the dipole and at equal distances from it. The fields at A and B are A and B.
(a) A = B
(b) A=2B
(c) A=-2B
(d) |EB|=1/2|EA|, and B perpendicular to A
Ans. (c)
Q.3
an electric dipole of moment is placed in a uniform electric field , with parallel to . It is then rotted by an angle q. The work done is
(a) pE sin q
(b) pE cosq
(c) pE(1-cosq)
(d) pE(1-sin T)
Ans. (c)
Q. 4
In which of the following states is the potential energy of an electric dipole maximum ?
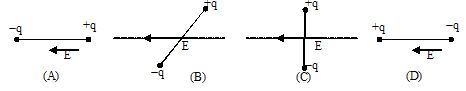
Ans (a)
Q.5
An electric dipole of moment p is placed normal to the lines of force of electric field E, then the work done in deflecting it through an angle of 180 degrees is
(1) pE
(2) + 2pE
(3) –
(4) Zero
Ans. (4)
Q.6
An electric dipole is placed in an uniform electric field such that the dipole moment makes an angle b ( ¹ 0) with The force and torque acting on the dipole are respectively given by
(1) \displaystyle 0,\,\,\overrightarrow{{p\,}}\times \overrightarrow{{E\,}}
(2) \displaystyle \overrightarrow{{p\,}}\cdot \overrightarrow{{E\,}},\,\,\,\overrightarrow{{p\,}}\times \overrightarrow{{E\,}}
(3) \displaystyle \overrightarrow{{p\,}}\times \overrightarrow{{E\,}},\,\,0
(4) \displaystyle \overrightarrow{{p\,}}\times \overrightarrow{{E\,}},\,\,\overrightarrow{{E\,}}\times \overrightarrow{{p\,}}
Ans. (1)
Q.7
An electric dipole is put in north-south direction in a sphere filled with water. Which statement is correct?
(1) Electric flux is coming towards sphere
(2) Electric flux is coming out of sphere
(3) Electric flux entering into sphere and leaving the sphere are same
(4) Water does not permit electric flux to enter into sphere.
Ans. (3)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
Q.1
An electric dipole is placed at the orgin and is directed along the x-axis. At a point P, far away from the dipole, the electric field is parallel to the y-axis. OP makes an angle q with the x-axis,
(a) tan q=Ö3 (b) tan q= Ö2 (c) q= 45° (d) tan q=1/Ö2
Ans. (b)
Q.2
Electric charges q, q and -2q are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle ABC of side L. The magnitude of electric dipole moment of the system is
(A) qL (B) 2qL (C) (Ö3)qL (D) 4qL
Ans. (C)
Q.3
An electric dipole is kept in non-uniform electric field. It experiences
(a) A force and a torque
(b) A force but not a torque
(c) A torque but not a force
(d) Neither a force nor a torque
Ans. (a)
Q.4
Three electric charges 2q each are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle ABC of side l. Another charge -6q is placed at the centroid of the triangle. The magnitude of electric dipole moment of the system is
(a) q
(b) 2ql
(c) \displaystyle \sqrt{3}ql
(d) zero
Ans. (d)
Q.5
If the magnitude of intensity of electric field at a distance x on axial line and at a distance y on equatorial line on a given dipole are equal, then x : y is
(a) 1 : 1
(b) \displaystyle 1:\sqrt{2}
(c) 1 : 2
(d) \displaystyle \sqrt[3]{2}:1
Ans. (d)
Q.6
For a dipole \displaystyle q=2\times {{10}^{{-6}}}C and d = 0.01 m. Calculate the maximum torque for this dipole if \displaystyle E=5\times {{10}^{5}}N/C
(a) \displaystyle 1\times {{10}^{{-3}}}N{{m}^{{-1}}}
(b) \displaystyle 10\times {{10}^{{-3}}}N{{m}^{{-1}}}
(c) \displaystyle 10\times {{10}^{{-3}}}Nm
(d) \displaystyle 1\times {{10}^{2}}N{{m}^{2}}
Ans. (c)
Q.7
An electric dipole is placed along the x-axis at the origin O. A point P is at a distance of 20cm from this origin such that OP makes an angle \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{3} with the x-axis. If the electric filed at P makes an angle θ with x-axis, the value of θ would be
(a) \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{3}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{3}+{{\tan }^{{-1}}}\left( {\frac{{\sqrt{3}}}{2}} \right)
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{2\pi }}{3}
(d) \displaystyle {{\tan }^{{-1}}}\left( {\frac{{\sqrt{3}}}{2}} \right)
Ans. (b)
Q.8
Two electric dipoles of moment P and 64 P are placed in opposite direction on a line at a distance of 25 cm. The electric field will be zero at point between the dipoles whose distance from the dipole of moment P is
(a) 5 cm
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{25}}{9}cm
(c) 10 cm
(d) \displaystyle \frac{4}{{13}}cm
Ans. (a)
Q.9
Two short dipoles \displaystyle p\,\hat{k} and \displaystyle \frac{p}{2}\,\hat{k} are located at (0, 0, 0) & (1m, 0, 2m) respectively. The resultant electric field due to the two dipoles at the point (1m, 0, 0) is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{9p}}{{32\,\pi \,{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}}\,\hat{k}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{-7p}}{{32\,\pi \,{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}}\,\hat{k}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{7p}}{{32\,\pi \,{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}}\,\hat{k}
(d) None of these
Ans. (b)
Q.10
An electric dipole is kept on the axis of a uniformly charged ring at distance from the centre of the ring. The direction of the dipole moment is along the axis. The dipole moment is p, charge of the ring is Q & radius of the ring is R. The force on the dipole is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{p\,Q}}{{3\,\pi \,{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}\,{{R}^{2}}}}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{4p\,Q}}{{3\,\pi \,{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\sqrt{3}\,{{R}^{2}}}}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{p\,Q}}{{3\,\pi \,{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\,{{R}^{2}}}}
(d) zero
Ans. (d)
Q.11
The force acting between two dipoles is proportional to xn . Where x is their mutual distance and n is
(a) -4 (b) -3 (c) 4 (d) -2
Ans. (a)
Q.12
In which of the following states is the potential energy of an electric dipole maximum ?
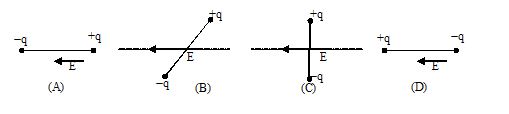
Ans. (a)
Q.13
Two connected charges of +q and -q respectively are at fixed distance AB apart in a non uniform electric field whose lines of force are shown in the figure
The resultant effect on the two charges is
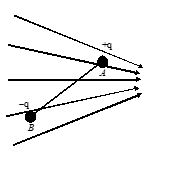
(A) a torque vector in the plane of the paper and no resultant force.
(B) a resultant force in the plane of the paper and no torque.
(C) a torque vector normal to the plane of the paper and no resultant force.
(D) a torque vector normal to the plane of the paper and a resultant force in the plane of the paper.
Ans. (d)
Q.14
We have two electric dipoles. Each dipole consists of two equal and opposite point charges at the end of an insulating rod of length d. The dipoles are placed along the x‑axis at a large distance r apart oriented as shown. The dipole on the left
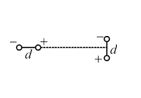
(a) will feel a force upwards and a torque trying to make it rotate clockwise.
(b) will feel a force upwards and a torque trying to make it rotate counterclockwise.
(c) will feel a force upwards and no torque about its centre.
(d) will feel a force downwards and a torque trying to make it rotate clockwise.
Ans. (b)
Q.15
Three charges of (+2q), (–q) and (–q) are placed at the corners A, B and C of an equilateral triangle of side a as shown in the adjoining figure. Then the dipole moment of this combination is
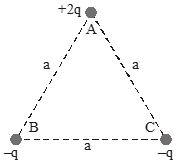
(a) \displaystyle qa
(b) Zero
(c) \displaystyle qa\sqrt{3}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{2}{{\sqrt{3}}}qa
Ans. (c)
16.
Half part of ring is uniformly positively charged and other half is uniformly negatively charged. Ring is in equilibrium in uniform electric field as shown and free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to plane. The equilibrium is
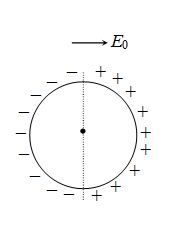
(a) stable
(b) unstable
(c) neutral
(d) can be stable or unstable
Ans (a)
17.
The magnitude of electric field intensity at point B (2, 0, 0) due to a dipole of dipole moment, \vec{P}=\hat{i}+\sqrt{3}\hat{j}kept at origin is (assume that the point B is at large distance from the dipole and k=\frac{1}{{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}})
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{\sqrt{{13}}k}}{8}
(b) \frac{{\sqrt{{13}}k}}{4}
(c) \frac{{\sqrt{7}k}}{8}
(d) \frac{{\sqrt{7}k}}{4}
Ans (c)
18.
A dipole of dipole moment p is kept at the centre of a ring of radius R and charge q. The dipole moment has direction along the axis of the ring. The resultant force on the ring due to the dipole is
(a) zero
(b) \frac{{pq}}{{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{R}^{3}}}}
(c) \frac{{pq}}{{2\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{R}^{3}}}}
(d) \frac{{pq}}{{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}{{R}^{3}}}}only if the charge is uniformly distributed on the ring.
Ans (b)
Comprehension Based Questions (19 and 20)
A dipole consists of two point charges ±2 nC separated by 4 cm.
19.
What is the dipole moment ?
(i) 9 x 10–11 C-m
(ii) 8 x 10–11 C-m
(iii) 6 x 10–11 C-m
(iv) 3 x 10–11 C-m
Ans (ii)
20.
What is the change in potential energy when the dipole rotates from alignment along a field E =105 N/C to an orientation 90° to E?
(i) 2 x 10–6 J
(ii) 8 x 10–6 J
(iii) 10 x 10–6 J
(iv) 5 x 10–6 J
Ans (ii)
