Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
Q.1
A thin convergent glass lens (mg = 1.5) has a power of +5.0 D. when this lens is immersed in a liquid of refractive index ml, it acts as a divergent lens of focal length 100 cm. The value of ml is
(a) 4/3 (b) 5/3 (c) 5/4 (d) 6/5
Ans. (b)
Q.2
Focal length of an equiconvex lens is 20 cm. If we cut it once perpendicular to principle axis, and then along principle axis. Then focal length of each part will be
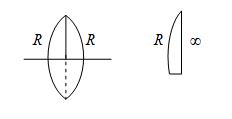
(a) 20 cm (b) 10 cm (c) 40 cm (d) 5 cm
Ans. (c)
Q.3
A liquid of refractive index 1.33 is placed between two identical plano-convex lenses, with refractive index 1.50. Two possible arrangements, P and Q are shown. The system is
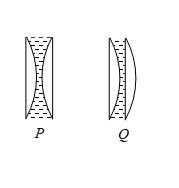
(a) divergent in P , convergent in Q
(b) convergent in P, divergent in Q
(c) convergent in both
(d) divergent in both
Ans. (c)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
Q.1
A plastic hemisphere has a radius of curvature of 8 cm and an index of refraction of 1.6. On the axis halfway between the plane surface and the spherical one (4 cm from each) is a small object O. The distance between the two images when viewed along the axis from the two sides of the hemisphere is approximately
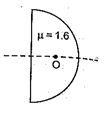
(a) 1.0 cm
(b) 1.5 cm
(c) 3.75 cm
(d) 2.5 cm
Ans (d)
Q.2
A beam of diameter ‘d’ is incident on a glass hemisphere as shown. If the radius of curvature of the hemisphere is very large in comparison to d, then the diameter of the beam at the base of the hemisphere will be
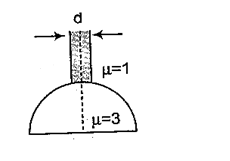
(a) \displaystyle \frac{3}{4}d
(b) d
(c) \displaystyle \frac{d}{3}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{2}{3}d
Ans (c)
Q.3
The image of point P when viewed from top of the slabs will be
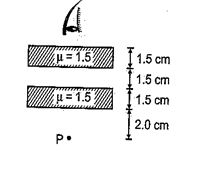
(a) 2.0 cm above P
(b) 1.5 cm above P
(c) 2.0 cm below P
(d) 1 cm above P
Ans (d)
Q.4
Two plano-convex lenses of glass of refractive index 1.5 have radii of curvature 20 cm and 30 cm respectively. They are placed in contact with the curved surfaces towards each other and the space between them is filled with water (m = 4/3). The focal length of the combination is
(a) -60 cm (b) 72 cm (c) 70 cm (d) 60.3 cm
Ans. (b)
Q.5
A thin convergent glass lens (mg = 1.5) has a power of +5.0 D. When this lens is immersed in a liquid of refractive index ml, it acts as a divergent lens of focal length 100 cm. The value of ml is
(a) 4/3 (b) 5/3 (c) 5/4 (d) 6/5
Ans. (b)
Q.6
Diameter of the flat surface of a circular plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the center is 3 mm. The radius of curvature of the curved part is
(a) 15 cm (b) 20 cm (c) 30 cm (d) 10 cm
Ans. (a)
Q.7
A sphere of radius R made of transparent material of refractive index m works like a thin lens having its optical center coinciding with the center of the sphere. The focal length of this thin lens is
(a) \frac{{\mu R}}{{\left( {\mu -1} \right)}}
(b) \frac{{\mu R}}{{2\left( {\mu -1} \right)}}
(c) \frac{{\mu R}}{{\left( {\mu +1} \right)}}
(d) \frac{{\left( {\mu -1} \right)R}}{{\left( {\mu +1} \right)}}
Ans. (b)
Q.8
Refraction takes place at a convex spherical boundary separating air-glass medium. For the image to be real, the object distance ( \displaystyle {{\mu }_{g}}=3/2). (Object is lying in the glass)
(a) should be greater than three times the radius of curvature of the refracting surface
(b) should be greater than two times the radius of curvature of the refracting surface
(c) should be greater than the radius of curvature of the refracting surface
(d) is independent of the radius of curvature of the refracting surface
Ans. (a)
Q.9
A plano convex lens fits exactly into a plano concave lens. Their plane surfaces are parallel to each other. If the lenses are made of different materials of refractive indices \displaystyle {{\mu }_{1}} and \displaystyle {{\mu }_{2}} and R is the radius of curvature of the curved surface of the lenses, then focal length of the combination is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{R}{{{{\mu }_{1}}-{{\mu }_{2}}}}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{2R}}{{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{R}{{2\left( {{{\mu }_{1}}-{{\mu }_{2}}} \right)}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{R}{{2-\left( {{{\mu }_{1}}+{{\mu }_{2}}} \right)}}
Ans. (a)
Q.10
The x-z plane separates two media A and B of refractive indices \displaystyle {{\mu }_{1}}=1.5\,\,and \displaystyle {{\mu }_{2}}=2\,\,. A ray of light travels from A to B. Its directions in the two media are given by unit vectors \displaystyle {{\vec{u}}_{1}}\,=\,a\hat{i}\,+\,b\hat{j} and \displaystyle {{\vec{u}}_{2}}\,=\,c\hat{i}\,+\,d\hat{j}Then
(a) \displaystyle \frac{a}{c}=\frac{4}{3}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{a}{c}=\frac{3}{4}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{b}{d}=\frac{4}{3}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{b}{d}=\frac{3}{4}
Ans. (a)
Comprehension Based Question (11 and 12)
The curved surface of a thin plano-convex lens (n = 1.5) has a 12 cm radius of curvature. Locate the image of an object in air at infinity given that the surface that faces the object is
11.
curved
(a)24 cm
(b)30 cm
(c)20 cm
(d)35 cm
Ans (a)
12
flat.
(a)30 cm
(b)24 cm
(c)50 cm
(d)20 cm
Ans (b)
13.
A thin biconvex lens is made of glass (n = 1.5) with surface of radii of curvature 12 cm and 16 cm. An object is located 20cm from the lens. What are the position and linear magnification of the image?
(a)43.64 cm, 2.18
(b)43.50 cm, 2.00
(c)42.50 cm, 1.50
(d)50.00 cm, 2.00
Ans (d)
14.
A long cylindrical tube containing water is closed by an equiconvex lens of focal length 10 cm in air. A point source is placed along the axis of the tube outside it at a distance of 21 cm from the lens. Locate the final image of the source. Refractive index of the material of the lens = 1.5 and that of water = 1.33.
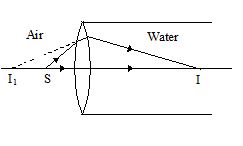
(a) 70 cm inside the tube
(b) 50 cm inside the tube
(c) 40 cm inside the tube
(d) 30 cm inside the tube
Ans (a)
