Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
Q.1
A concave mirror of focal length f produces an image n times the size of the object. If the image is real then the distance of the object from the mirror is
(a) \left( {n-1} \right)f
(b) \frac{{\left( {n-1} \right)}}{n}f
(c) \frac{{\left( {n+1} \right)}}{n}f
(d) \left( {n+1} \right)f
Ans. (c)
Q.2
For a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm, if the object is at a distance of 30 cm from the pole, then the nature of the image and its magnification will be
(a) real and –2
(b) virtual and –2
(c) real and +2
(d) virtual and +2
Ans. (a)
Q.3
The relation between lateral magnification m, object distance u and focal length f of a spherical mirror is
(a) m=\frac{{f-u}}{f}
(b) m=\frac{f}{{f+u}}
(c) m=\frac{{f+u}}{f}
(d) m=\frac{f}{{f-u}}
Ans. (d)
Q.4
An object 1 cm tall is placed in front of a mirror at a distance of 4 cm. In order to produce an upright image of 3cm height one needs a
(a) convex mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(b) concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(c) concave mirror of radius of curvature 4 cm
(d) plane mirror of height 12 cm\
Ans. (b)
Q.5
An object is placed at 20 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm. The image formed by the mirror is
(a) Real and at 20 cm from the mirror
(b) Virtual and at 20 cm from the mirror
(c) Virtual and at (20/3) cm from the mirror
(d) Real and at (20/3) cm from the mirror
Ans. (c)
Q.6
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, there is no parallax between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of curvature of the convex mirror (in cm) is
(a) 60 (b) 50 (c) 30 (d) 25
Ans. (d)
Q.7
Rays are converging towards a convex mirror, final image will be
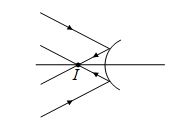
(a) real
(b) virtual
(c) may be real or virtual
(d) image will not form
Ans. (a)
8.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 36cm. At what position should an object be placed for its image to be erect and be magnified by a factor of three?
(a) 20 cm
(b) 22 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 30 cm
Ans (c)
9.
An object of height 0.5 cm is placed 18 cm from a curved mirror. The erect image is 2 cm high. What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(a) 50 cm
(b) 10 cm
(c) 30 cm
(d) 24 cm
Ans (d)
10.
A real object 27 cm from a concave mirror produces a real image 15.9 cm from the mirror. What is the image position for an object placed 15 cm from the mirror?
(a) 50 cm
(b) 10 cm
(c)30 cm
(d)100 cm
Ans (c)
11.
An object is 60 cm from a concave mirror. The size of the real image is 40% of the size of the object. What is the radius of curvature of the mirror?
(a)34.3 cm
(b)32.0 cm
(c) 25.5 cm
(d) 50.0 cm
Ans (a)
12.
A convex mirror of focal length 30cm produces an image with a magnification
of 0.4. Where is the object?
(a)45 cm
(b)90 cm
(c)25 cm
(d) 50 cm
Ans (a)
13.
A concave mirror produces an image 40% larger when a real object is 20cm from the mirror. Determine the possible focal lengths of the mirror.
(a)10.5 cm; 50 cm
(b)11.7 cm; 70 cm
(c)12.5 cm; 80 cm
(d)13.7 cm; 90 cm
Ans (c)
14.
The longitudinal magnification `mL’ for a very small object and linear magnification `m’ for a mirror are related as
(a)mL=m
(b) mL=(m)1/2
(c)mL=m2
(d) mL=m3.
Ans : (c)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
Q.1
An object is placed at a distance u from a concave mirror and its real image is received on a screen placed at a distance of v from the mirror. If f is the focal length of the mirror, then the graph between 1/v versus 1/u is
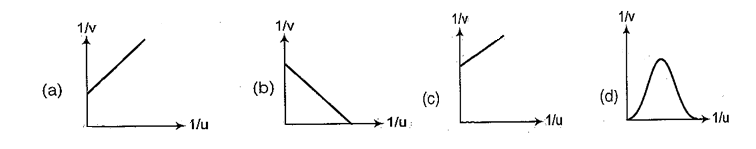
Ans (b)
Q.2
In the figure shown, the image of a real object is formed at point I. AB is the principal axis of the mirror. The mirror must be
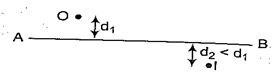
(a) concave and placed towards right of I
(b) concave and placed towards left of I
(c) convex and placed towards right of I
(d) convex and placed towards left of I
Ans (a)
Q.3
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length f as shown in figure. Choose the correct shape of the image.
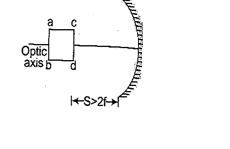
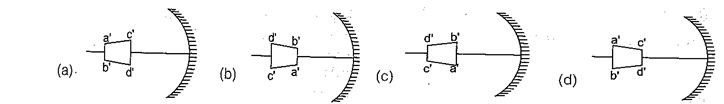
Ans (b)
Q.4
A point object is kept between a plane mirror and a concave mirror facing each other. The distance between the mirrors is 22.5 cm. The radius of curvature of the concave mirror is 20 cm. What should be the distance of the object from the concave mirror so that after two successive reflections the final image is formed on the object itself? (Consider first reflection from concave mirror.)
(a) 5 cm (b) 15 cm (c) 10 cm (d) 7.5 cm
Ans. (b)
Q.5
A luminous point object is moving along the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm towards it. When its distance from the mirror is 20 cm its velocity is 4 cm/s. The velocity of the image in cm/s at that instant is
(a) 6, towards the mirror
(b) 6, away from the mirror
(c) 9, away from the mirror
(d) 9, towards the mirror
Ans. (c)
Q.6
The passenger side-view mirror on an automobile often has the notation ‘objects seen in mirror are closer than they appear’. Is the image really farther away than the object?
(a) Yes, the image is smaller and farther away than the object.
(b) No, the image is smaller and closer than the object.
(c) No, the image is larger and closer than the object.
(d) Yes, the image is larger and farther away than the object.
Ans. (b)
Q.7
Focal length of a convex mirror is 10 cm
(a) image of an object placed at 20 cm is also at 20 cm
(b) image of an object placed at 10 cm is at infinity
(c) both (a) and (b) are wrong
(d) both (a) and (b) are correct
Ans. (c)
Q.8
A concave mirror has a focal length 20 cm. The distance between the two positions of the object for which the image size is double of the object size is
(a) 20 cm (b) 40 cm (c) 30 cm (d) 60 cm
Ans. (a)
Q.9
An infinitely long rod lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length f. The near end of the rod is at a distance \displaystyle u\,>\,f from the mirror. Its image will have a length
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{uf}}{{u-f}}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{uf}}{{u+f}}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{{{f}^{2}}}}{{u+f}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{{{{f}^{2}}}}{{u-f}}
Ans. (d)
Q.10
An object is placed infront of a concave mirror of focal length f. A virtual image is formed with a magnification of 2. To obtain a real image of same magnification, the object has to move by a distance
(a) f (b) f/2 (c) 3f/2 (d) 2f/3
Ans. (a)
