Video Lecture
Theory For Notes Making
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Objective Assignment
Q.1
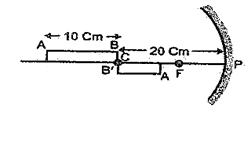
A concave mirror of focal length f produces an image n times the size of the object. If the image is real then the distance of the object from the mirror is
(a) \left( {n-1} \right)f
(b) \frac{{\left( {n-1} \right)}}{n}f
(c) \frac{{\left( {n+1} \right)}}{n}f
(d) \left( {n+1} \right)f
Ans. (c)
Q.2
For a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm, if the object is at a distance of 30 cm from the pole, then the nature of the image and its magnification will be
(a) real and –2
(b) virtual and –2
(c) real and +2
(d) virtual and +2
Ans. (a)
Q.3
The relation between lateral magnification m, object distance u and focal length f of a spherical mirror is
(a) m=\frac{{f-u}}{f}
(b) m=\frac{f}{{f+u}}
(c) m=\frac{{f+u}}{f}
(d) m=\frac{f}{{f-u}}
Ans. (d)
Q.4
An object 1 cm tall is placed in front of a mirror at a distance of 4 cm. In order to produce an upright image of 3cm height one needs a
(a) convex mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(b) concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(c) concave mirror of radius of curvature 4 cm
(d) plane mirror of height 12 cm\
Ans. (b)
Q.5
An object is placed at 20 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm. The image formed by the mirror is
(a) Real and at 20 cm from the mirror
(b) Virtual and at 20 cm from the mirror
(c) Virtual and at (20/3) cm from the mirror
(d) Real and at (20/3) cm from the mirror
Ans. (c)
Q.6
An object is placed in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 50 cm. A plane mirror is introduced covering the lower half of the convex mirror. If the distance between the object and the plane mirror is 30 cm, there is no parallax between the images formed by the two mirrors. The radius of curvature of the convex mirror (in cm) is
(a) 60 (b) 50 (c) 30 (d) 25
Ans. (d)
Q.7
Rays are converging towards a convex mirror, final image will be
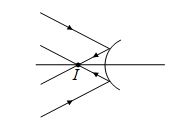
(a) real
(b) virtual
(c) may be real or virtual
(d) image will not form
Ans. (a)
8.
A concave mirror has a focal length of 36cm. At what position should an object be placed for its image to be erect and be magnified by a factor of three?
(a) 20 cm
(b) 22 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 30 cm
Ans (c)
9.
An object of height 0.5 cm is placed 18 cm from a curved mirror. The erect image is 2 cm high. What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(a) 50 cm
(b) 10 cm
(c) 30 cm
(d) 24 cm
Ans (d)
10.
A real object 27 cm from a concave mirror produces a real image 15.9 cm from the mirror. What is the image position for an object placed 15 cm from the mirror?
(a) 50 cm
(b) 10 cm
(c)30 cm
(d)100 cm
Ans (c)
11.
An object is 60 cm from a concave mirror. The size of the real image is 40% of the size of the object. What is the radius of curvature of the mirror?
(a)34.3 cm
(b)32.0 cm
(c) 25.5 cm
(d) 50.0 cm
Ans (a)
12.
A convex mirror of focal length 30cm produces an image with a magnification
of 0.4. Where is the object?
(a)45 cm
(b)90 cm
(c)25 cm
(d) 50 cm
Ans (a)
13.
A concave mirror produces an image 40% larger when a real object is 20cm from the mirror. Determine the possible focal lengths of the mirror.
(a)10.5 cm; 50 cm
(b)11.7 cm; 70 cm
(c)12.5 cm; 80 cm
(d)13.7 cm; 90 cm
Ans (c)
14.
The longitudinal magnification `mL’ for a very small object and linear magnification `m’ for a mirror are related as
(a)mL=m
(b) mL=(m)1/2
(c)mL=m2
(d) mL=m3.
Ans : (c)
Subjective Assignment
Q.1
A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
Q.2
A 4.5 cm needle is placed 12 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
Q.3
An object of 3 cm height is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
Q.4
Use the mirror equation to show that
(a) an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.
(b) A convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
(c) An object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
Q.5
(a) Draw the ray diagram for the formation of image of an object by a convex mirror and use it (along with the sign convention) to derive the ‘mirror formula’.
(b) Use the mirror formula to show that for an object, kept between the pole and focus of a concave mirror, the image appears to be formed behind the mirror.
Q.6
(a) Derive the ‘mirror equation’ using the ray diagram for the formation of a real image by a concave mirror.
Q.7
Use the mirror equation to deduce that:
(a) an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2f.
(b) a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
(c) the virtual image produced by a convex mirror is always diminished in size and is located between the focus and the pole.
(d) an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror produces a virtual and enlarged image.
Q.8
Answer the following questions:
(a) You have learnt that plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of objects. Can they produce real images under some circumstances? Explain.
9.
An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure.
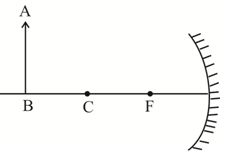
(i)
Complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object.
(ii)
How will the position and intensity of the image be affected if the lower half of the mirror’s reflecting surface is painted black
10.
A rod AB = 10 cm in length is placed along the principal axis of a concave mirror having focal length equal to 10 cm as shown in fig. The distance PB = 20 cm. What is the length of the image of the rod AB?