Video Lecture
Theory For Making Notes
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Practice Questions (Level-1)
Q.1
The reactance of a 25 µF capacitor at the AC frequency of 4000 Hz is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{5}{\pi }\Omega
(b) \displaystyle \sqrt{{\frac{5}{\pi }}}\Omega
(c) \displaystyle 10\,\Omega
(d) \displaystyle \sqrt{{10}}\,\Omega
Ans. (a)
Q.2
What will be the approximate resistance offered by a capacitor of 10 µF and frequency 100 Hz ?
(a) 160 Ω (b) 1600 Ω (c) 16 Ω (d) None of the above
Ans. (a)
Q.3
An AC voltage is applied to a resistance R and an inductor L in series. If R and the inductive reactance are both equal to 3Ω, the phase difference between the applied voltage and the current in the circuit is
(a) π / 4 (b) π / 2 (c) zero (d) π / 6
Ans. (a)
Q.4
The power factor of an R–L circuit is \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{2}}}. If the frequency of AC is doubled, what will be the power factor ?
(a) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{3}}}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{5}}}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{7}}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{\sqrt{{11}}}}
Ans. (b)
Q.5
An inductive coil has a resistance of 100 Ω. When an AC signal of frequency 1000 Hz is applied to the coil, the voltage leads the current by 45º. The inductance of the coil is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{10\pi }}
(b) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{20\pi }}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{40\pi }}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{60\pi }}
Ans. (b)
Q.6
Two coils have a mutual inductance 0.005 H. The current changes in the first coil according to equation \displaystyle I={{I}_{0}}\,\sin \,\omega t, where \displaystyle {{I}_{0}}=10A and \displaystyle \omega =100\pi \,rad/s. The maximum value of emf in the second coil is (in volt).
(a) 2 \displaystyle \pi
(b) 5 \displaystyle \pi
(c) \displaystyle \pi
(d) 4 \displaystyle \pi
Ans. (b)
Q.7
In an AC circuit, V and I are given by V = 150 sin (150 t) volt and \displaystyle I=150\sin \left( {150\,t+\frac{\pi }{3}} \right) The power dissipated in the circuit is
(a) 106 W (b) 150 W (c) 5625 W (d) zero
Ans. (c)
Q.8
In an AC circuit an alternating voltage \displaystyle e=200\sqrt{2}\sin 100\,tvolt is connected to a capacitor of capacity 1µF. The rms value of the current in the circuit is
(a) 100 mA (b) 200 mA (c) 20 mA (d) 10 mA
Ans. (c)
Q.9
An AC voltage is applied to a resistance R and an inductor L in series. If R and the inductive reactance are both equal to 3Ω, the phase difference between the applied voltage and the current in the circuit is
(a) π/4 (b) π/2 (c) zero (d) π/6
Ans. (a)
Q.10
In the case of an inductor
(a) voltage lags the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}
(b) voltage leads the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{2}
(c) voltage leads the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{3}
(d) voltage leads the current by \displaystyle \frac{\pi }{4}
Ans. (b)
Q.11
The inductive time constant in an electrical circuit is
(a) \displaystyle L\,R
(b) \displaystyle \frac{L}{R}
(c) \displaystyle \sqrt{{\frac{L}{R}}}
(d) \displaystyle \frac{R}{L}
Ans. (b)
Q.12
In an AC circuit, V and i are given by V = 100 sin (100 t) volt and \displaystyle i=100\sin \left( {100\,t+\frac{\pi }{3}} \right)amp The power dissipated in the circuit is
(a) 104 W (b) 2.5 kW (c) 5 kW (d) 5 W
Ans. (b)
Q.13
The reactance of 25 µF capacitor at the AC frequency of 4000 Hz is
(a) \displaystyle \frac{5}{\pi }Ω
(b) \displaystyle \sqrt{{\frac{5}{\pi }}}Ω
(c) 10 Ω
(d) \displaystyle \sqrt{{10}}Ω
Ans. (a)
Q.14
The frequency for which a 5 µF capacitor has a reactance of \displaystyle \frac{1}{{1000}}Ω is given by
(a) \displaystyle \frac{{100}}{\pi }MHz
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{1000}}{\pi }Hz
(c) \displaystyle \frac{1}{{1000}}Hz
(d) 1000 Hz
Ans. (a)
Q.15
The capacity of a pure capacitor is 1 F. In DC circuits, its effective resistance will be
(a) zero (b) infinite (c) 1 Ω (d) 1/2 Ω
Ans. (b)
Q.16
The rms voltage of the wave form shown is
(a) 10 V
(b) 7 V
(c) 6.37 V
(d) None of these
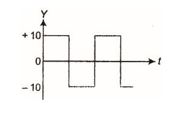
Ans. (a)
Q.17
The output sinusoidal current versus time curve of a rectifier is shown in the figure. The average value of output current in this case is
(a) 0
(b) \displaystyle \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{2}
(c) \displaystyle \frac{{2{{I}_{0}}}}{\pi }
(d) \displaystyle {{I}_{0}}
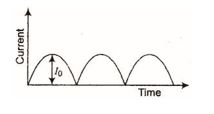
Ans. (c)
18.
The capacitor reactance of a capacitor in d.c. circuit in ohms is
(A) \frac{1}{{\omega C}}
(B) \displaystyle \omega C
(C) zero
(D) \displaystyle \infty
Ans (A)
19.
The reactance of a inductor at 50 Hz is 10 \displaystyle \Omega . What will be its reactance at 200 Hz ?
(A) 10 \displaystyle \Omega
(B) 40 \displaystyle \Omega
(C) 2.5 \displaystyle \Omega
(D) 20 \displaystyle \Omega
Ans (B)
20.
An inductive circuit contains a resistance of 10 \displaystyle \Omega and inductance of 2H. If an a.c. voltage of 120 V and frequency 60 Hz is applied to this circuit, the current in circuit would be nearly
(A) 0.32 A
(B) 0.16 A
(C) 0.48 A
(D) 0.80 A
Ans (B)
21.
What is the average value of a.c. over a half cycle
(A) zero
(B) \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{\pi }
(C) \displaystyle \frac{{2{{I}_{0}}}}{\pi }
(D) none of these
Ans (C)
22.
In an AC circuit having R and L in serries
(A) voltage leads current
(B) current leads voltage
(C) voltage and current are increase
(D) voltage and current are in opposite phase
Ans (A)
23.
Average power in a pure inductive circuit is
(A) irms´ vrms
(B) 2 irms´ vrms
(C) 1
(D) zero
Ans (D)
24.
The root mean square value of voltage (V) in an AC circuit is
(A) 0.637Vmax
(B) 0.707 Vmax
(C) 2Vmax
(D) \sqrt{2}Vmax
Ans (B)
25.
In an AC series circuit, instantaneous voltage is maximum while instantaneous current is zero. The source is connected to
(A) pure inductor only
(B) pure resistance only
(C) pure capacitor only
(D) (A) or (C)
Ans (D)
26.
In the circuit shown, the voltage in C & L are
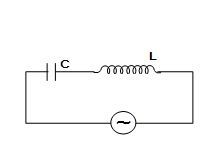
(A) out of phase by \displaystyle \pi
(B) out of phase by \displaystyle \pi /2
(C) out of phase by \displaystyle \pi /4
(D) In Phase
Ans (A)
27.
If the mean value of an alternating voltage is \frac{{28\sqrt{2}}}{\pi } volt, its rms value is
(A) 28 volt
(B) 14 volt
(C) 14 \sqrt{2} volt
(D)zero
Ans (B)
28.
When an alternating voltage source is connected to a pure inductor, the difference between phase of instantaneous current through the inductor and the phase of instantaneous potential difference across the inductor at t = T/4 sec. is
(A)zero
(B) \displaystyle \pi /2 rad.
(C) – \displaystyle \pi /2 rad.
(D) \displaystyle \pi /4 rad.
Ans (C)
Practice Questions (Level-2)
1.
An alternating current is given by i = i1 cos \displaystyle \omega t + i2 sin \displaystyle \omega t. The rms current is given by
(A) i1 + i2
(B) ( \sqrt{{{{i}_{1}}}}+\sqrt{{{{i}_{2}}}})2
(C) \frac{{{{i}_{1}}+{{i}_{2}}}}{2}
(D) none of the above
Ans (D)
2.
The current in a series RL circuit decays as I={{I}_{0}}{{e}^{{-t/\tau }}}. Obtain the rms current in the interval 0\le t\le \tau .
(a) \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{2}
(b) \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{e}
(c) \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{{\sqrt{2}e}}
(d) \frac{{{{I}_{0}}}}{e}\sqrt{{\frac{{{{e}^{2}}-1}}{2}}}
Ans (d)
3.
An alternating voltage is given by e={{e}_{1}}\sin \omega t+{{e}_{2}}\cos \omega t. Then, the root mean square value of voltage is given by
(a) \sqrt{{e_{1}^{2}+e_{2}^{2}}}
(b) \sqrt{{{{e}_{1}}+{{e}_{2}}}}
(c) \sqrt{{\frac{{{{e}_{1}}{{e}_{2}}}}{2}}}
(d) \sqrt{{\frac{{e_{1}^{2}+e_{2}^{2}}}{2}}}
Ans (d)
